Clinical Efficacy and Transcriptomic Study on the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease Angina of Qi Deficiency and Blood Stasis Type with Maitong Jun'an Decoction
-
摘要:
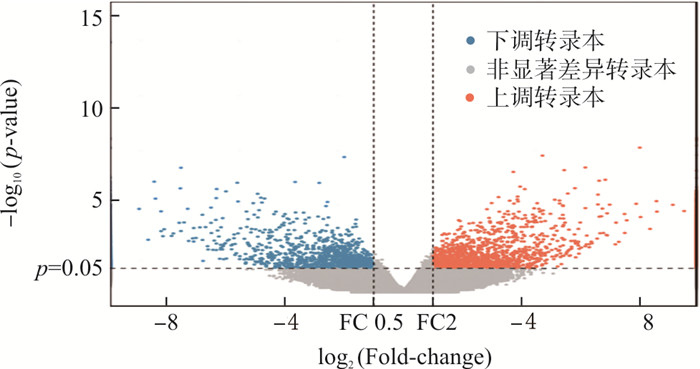
目的 观察脉通君安汤治疗气虚血瘀型冠心病心绞痛的临床疗效, 并通过转录组学方法初步阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 将符合纳入标准的140例气虚血瘀型冠心病心绞痛患者依据随机数字法分为治疗组、对照组各70例, 治疗期间对照组脱落3例。对照组予冠心病二级预防西医基础治疗, 治疗组在对照组治疗基础上加服脉通君安汤, 2组疗程均为8周。治疗前后评估2组患者中医证候积分、加拿大心血管学会(Canadian cardiovascular society, CCS)心绞痛分级、西雅图量表(Seattle angina questionnaire, SAQ)评分、焦虑自评量表(Self-rating anxiety scale, SAS)评分、抑郁自评量表(Self-rating depression scale, SDS)评分及不良反应, 并基于性别、年龄、病程相匹配原则选取9例患者治疗前后外周血进行转录组学测序。 结果 治疗后, 2组患者中医证候积分均明显下降(P < 0.01), 治疗组在改善胸痛、胸闷、气短、神倦乏力及总分方面优于对照组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);治疗组CCS心绞痛分级总改善率优于对照组(P < 0.05);2组治疗前后SAQ、SAS及SDS评分均显著改善(P < 0.01), 治疗组SAQ评分改善优于对照组(P < 0.05, P < 0.01)。转录组学结果显示, 治疗前后具有显著差异表达的mRNA有862个, 包括509个上调, 353个下调;GO分析结果显示差异表达的mRNA生物学过程有666条, 主要包括病毒基因表达、翻译启动、RNA分解代谢过程等,细胞组分112条, 主要包括黏着斑、核糖体亚基、核斑点等;分子功能有94条, 主要包括双链RNA结合、钙黏蛋白结合、转录共调节因子活性等;KEGG分析结果显示差异mRNA富集信号通路包括20条, 主要包括甘油磷脂代谢通路、单磷酸腺苷激活的蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)信号通路、核糖体通路等。 结论 脉通君安汤能够改善气虚血瘀型冠心病心绞痛患者临床症状,其作用机制为多靶点多通路,可能与甘油磷脂代谢通路、AMPK信号通路、核糖体通路的调节相关。 Abstract:OBJECTIVE To observe the clinical efficacy of Maitong Jun'an Decoction in treating coronary heart disease (CHD) angina of qi deficiency and blood stasis type, and preliminarily elucidate its possible mechanism of action through transcriptomics methods. METHODS A total of 140 patients with CHD angina of qi deficiency and blood stasis type were included and randomly divided into a treatment group and a control group, with 70 cases in each group. During the treatment period, 3 patients in the control group dropped out. The control group received basic Western medicine treatment for secondary prevention of CHD, while the treatment group received Maitong Jun'an Decoction in addition to the treatment in the control group. The treatment period for both groups was 8 weeks. Before and after treatment, the patients in both groups were evaluated for the TCM syndrome score, Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) angina grading, Seattle angina questionnaire (SAQ) score, self-rating anxiety scale (SAS), self-rating depression scale (SDS) score, and adverse reactions. The peripheral blood of 9 patients before and after treatment was selected for transcriptomic sequencing based on the principle of gender, age, and disease duration matching. RESULTS After treatment, the TCM syndrome scores and total scores of the 2 groups were significantly reduced(P < 0.01). The treatment group was better than the control group in improving chest pain, chest tightness, shortness of breath, fatigue and total score (P < 0.05, P < 0.01); the overall improvement rate of CCS angina grading in the treatment group was better than that in the control group (P < 0.05); the SAQ, SAS and SDS scores of the 2 groups were significantly reduced before and after treatment (P < 0.01), and the SAQ score of the treatment group was improved better than that of the control group (P < 0.05, P < 0.01). The transcriptomics results showed that there were 862 significantly different mRNAs before and after treatment, including 509 up-regulated and 353 down-regulated. GO analysis showed that there were 666 biological processes in the differentially expressed mRNAs, mainly including viral gene expression, translation initiation, RNA catabolism, etc. There were 112 cell components, mainly including focal adhesion, ribosome subunit, nuclear spot, etc. There were 94 molecular functions, mainly including double-stranded RNA binding, cadherin binding, transcription co-regulatory factor activity, etc. KEGG analysis showed that the differentially expressed mRNAs enriched in 20 signaling pathways, mainly including glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, ribosome pathway, etc. CONCLUSION Maitong Jun'an Decoction can improve clinical symptoms in patients with CHD angina of qi deficiency and blood stasis type. Its mechanism of action is multi-target and multi pathway, mainly related to the regulation of glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, ribosome pathway. -
表 1 2组患者基线资料比较(x±s)
Table 1. Comparison of baseline information between 2 groups of patients(x±s)
组别 例数 男 女 年龄/岁 身高/cm 体质量/kg 病程/a 治疗组 70 58 12 60.40±8.30 169.70±5.80 69.90±9.70 3.64±1.32 对照组 67 46 21 62.90±7.90 168.00±4.90 69.30±8.10 3.42±1.96 组别 例数 合并症 CCS心绞痛分级 高血压 糖尿病 Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ 治疗组 70 37 24 16 41 13 对照组 67 24 22 19 36 12 注:CCS心绞痛分级标准[4],Ⅱ级:日常活动稍受限制,快步行走或上楼、登高、饭后行走或上楼、寒冷或风中行走、情绪激动可发作心绞痛,或在睡醒后数小时发作,正常情况下以一般速度平地步行200 m以上或登1层以上楼梯受限;Ⅲ级:日常活动明显受限,正常情况下以一般速度平地步行100~200 m或登1层楼梯时可发作心绞痛;Ⅳ级:轻微活动或休息时即可出现心绞痛症状。 表 2 2组患者治疗前后中医证候积分比较[M(P25, P75)]
Table 2. Comparison of TCM syndrome points before and after treatment in 2 groups [M(P25, P75)]
组别 例数 时间 胸痛 胸闷 气短 心悸 神倦乏力 自汗 不寐 总分 对照组 67 治疗前 4(4, 4) 4(4, 6) 2(2, 2) 2(2, 2) 2(2, 2) 1(1, 2) 2(1, 2) 18(16, 19) 治疗后 2(2, 4)** 2(2, 4)** 1(1, 2)** 1(1, 2)** 1(1, 1)** 0(0, 1)** 1(1, 2)** 10(9, 12)** 治疗组 70 治疗前 4(4, 6) 4(4, 6) 2(2, 2) 2(2, 3) 2(2, 2) 1(1, 2) 2(1, 2) 18(16, 20) 治疗后 2(0, 2)**# 2(2, 2)**## 1(1, 1)**## 1(1, 1)** 1(1, 1)**## 0(0, 1)** 1(1, 2)** 7(5, 9)**## 注: 组内比较, **P < 0.01;组间比较, #P < 0.05,##P < 0.01。 表 3 2组患者治疗后CCS心绞痛分级比较
Table 3. Comparison of CCS angina grading between 2 groups of patients after treatment
组别 例数 显效 有效 无效 加重 总改善率/% 对照组 67 20 20 19 8 59.70 治疗组 70 46 15 5 4 87.14# 注: 组间比较, χ2=20.401, #P < 0.05。 表 4 2组患者治疗前后SAQ量表评分比较[M(P25, P75)]
Table 4. Comparison of SAQ scale scores before and after treatment between 2 groups[M(P25, P75)]
组别 例数 时间 PL AS AF TS DP 对照组 67 治疗前 46.7(42.2, 48.9) 50.0(50.0, 50.0) 40.0(30.0, 50.0) 47.1(41.2, 52.9) 50.0(41.7, 58.3) 治疗后 60.0(55.6, 62.2)** 75.0(50.0, 75.0)** 50.0(50.0, 60.0)** 58.8(52.9, 64.7)** 66.7(58.3, 75.0)** 治疗组 70 治疗前 46.7(44.4, 48.9) 50.0(50.0, 50.0) 40.0(30.0, 50.0) 47.1(41.2, 52.9) 50.0(41.7, 58.3) 治疗后 71.1(68.9, 73.3)**## 75.0(75.0, 75.0)**# 70.0(60.0, 70.0)**## 82.4(76.5, 82.4)**## 83.3(75.0, 83.3)**## 注: 组内比较, **P < 0.01;组间比较, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01。 表 5 2组患者治疗前后SAS、SDS评分比较[M(P25, P75)]
Table 5. Comparison of SAS and SDS scores between 2 groups before and after treatment [M(P25, P75)]
组别 例数 时间 SAS评分 SDS评分 对照组 67 治疗前 39.0(36.0, 42.0) 44.0(40.5, 46.0) 治疗后 35.0(32.0, 38.0)** 38.0(33.0, 41.0)** 治疗组 70 治疗前 39.0(36.0,41.0) 44.0(40.0, 46.0) 治疗后 34.0(33.0,36.0)** 37.0(33.0, 40.0)** 注: 组内比较, **P < 0.01。 -
[1] WEIR H K, ANDERSON R N, COLEMAN KING S M, et al. Heart disease and cancer deaths-trends and projections in the United States, 1969-2020[J]. Prev Chronic Dis, 2016, 13: E157. [2] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2023, 38(6): 583-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2023.06.001The Writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. Report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2022[J]. Chin Circ J, 2023, 38(6): 583-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2023.06.001 [3] 李艳荣, 李瑞雪, 樊慧杰, 等. 转录组学技术在中医药领域的应用研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2022, 33(4): 943-947. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2022.04.50LI Y R, LI R X, FAN H J, et al. Application Research advances of Transcriptome Technology in the field of Traditional Chinese Medicine[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2022, 33(4): 943-947. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2022.04.50 [4] CAMPEAU L. Letter: Grading of angina pectoris[J]. Circulation, 1976, 54(3): 522-523. [5] 中华医学会心血管病学分会介入心脏病学组, 中华医学会心血管病学分会动脉粥样硬化与冠心病学组, 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会血栓防治专业委员会, 等. 稳定性冠心病诊断与治疗指南[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2018, 46(9): 680-694. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.09.004Interventional Cardiology Group of the Cardiovascular Disease Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, Atherosclerosis and Coronary Heart Disease Group of the Cardiovascular Disease Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, Thrombosis Prevention and Treatment Professional Committee of the Cardiovascular Physicians Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association, etc. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of stable coronary heart disease[J]. Chin J Cardiol, 2018, 46(9): 680-694. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.09.004 [6] 中华医学会心血管病学分会, 中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会. 慢性稳定性心绞痛诊断与治疗指南[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2007, 35(3): 195-206. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0253-3758.2007.03.002Cardiovascular Disease Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Editorial Committee of Chinese Journal of Cardiology. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of patients with chronic stable angina[J]. Chin J Cardiol, 2007, 35(3): 195-206. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0253-3758.2007.03.002 [7] 中药新药临床研究指导原则: 试行[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2002: 69-70.Guiding principles for clinical research of new Chinese medicine: Trial implementation[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 69-70. [8] 国家卫生计生委合理用药专家委员会, 中国药师协会. 冠心病合理用药指南(第2版)[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2018, 10(6): 1-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRFS202106031.htmNational Health and Family Planning Commission Rational Drug Use Expert Committee, Chinese Pharmacists Association. Guidelines for rational drug use in coronary heart disease (2nd Ed)[J]. Chin J Front Med Sci Electron Version, 2018, 10(6): 1-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JRFS202106031.htm [9] TSAO C W, ADAY A W, ALMARZOOQ Z I, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update: A report from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2023, 147(8): e93-e621. [10] 毕颖斐, 毛静远, 王贤良, 等. 中医药防治冠心病临床优势及有关疗效评价的思考[J]. 中医杂志, 2015, 56(5): 437-440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ201505027.htmBI Y F, MAO J Y, WANG X L, et al. Clinical advantages of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease and related curative effect evaluation[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2015, 56(5): 437-440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYZ201505027.htm [11] JACQUIER A. The complex eukaryotic transcriptome: Unexpected pervasive transcription and novel small RNAs[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2009, 10(12): 833-844. doi: 10.1038/nrg2683 [12] 张晓萌, 李健春, 王琼, 等. 转录组测序技术在中医药领域的应用[J]. 中国现代中药, 2016, 18(8): 1084-1087. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJXX201608033.htmZHANG X M, LI J C, WANG Q, et al. Application of transcriptome sequencing technology in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Mod Chin Med, 2016, 18(8): 1084-1087. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJXX201608033.htm [13] 齐婧, 尤金枝, 王永刚, 等. 冠心病"虚、瘀、痰、毒"致病浅析[J]. 新中医, 2014, 46(6): 258-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REND201406131.htmQI J, YOU J Z, WANG Y G, et al. A brief analysis of the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease caused by "deficiency, stasis, phlegm, and poison"[J]. J N Chin Med, 2014, 46(6): 258-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REND201406131.htm [14] 陈贵珺, 王恒和. 近5年我国冠心病中医证型地域分布规律研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2018, 45(6): 1142-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNZY201806006.htmCHEN G J, WANG H H. Study on regional distribution of TCM syndromes of coronary heart disease in recent 5 years in China[J]. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 45(6): 1142-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNZY201806006.htm [15] 葛永彬, 毛静远. 6 155例冠心病患者中医证型分布规律分析[J]. 北京中医药, 2014, 33(7): 533-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJZO201407024.htmGE Y B, MAO J Y. Analysis on the distribution of TCM syndrome types in 6 155 patients with coronary heart disease[J]. Beijing J Tradit Chin Med, 2014, 33(7): 533-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJZO201407024.htm [16] CAO Y, SHEN T, HUANG X Q, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide restores autophagic flux and improves cardiomyocyte function in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(3): 4837-4848. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13596 [17] JIANG M M, NI J Y, CAO Y L, et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury from oxidative stress by regulating succinate, lysophospholipid metabolism, and ROS scavenging system[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 9137654. [18] WEI W L, ZENG R, GU C M, et al. Angelica sinensis in China-a review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2016, 190: 116-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.023 [19] CHENG C Y, KAO S T, LEE Y C. Angelica sinensis extract protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the hippocampus by activating p38 MAPK-mediated p90RSK/p-Bad and p90RSK/CREB/BDNF signaling after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 252: 112612. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112612 [20] ZHAO D Y, YU D D, REN L, et al. Ligustilide protects PC12 cells from oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis via the LKB1-AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2020, 15(3): 473-481. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.266059 [21] 杨丽, 杨玲. 瓜蒌皮对冠心病的药理作用及其机制研究[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志, 2016, 3(37): 7495-7496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWX201637143.htmYANG L, YANG L. Pharmacological effect and mechanism of Trichosanthes kirilowii peel on coronary heart disease[J]. J Clin Med Lit, 2016, 3(37): 7495-7496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWX201637143.htm [22] 高源, 季伟, 肖丹, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨"红花-桃仁" 药对防治冠心病的作用机制[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2019, 21(10): 2180-2187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJKX201910025.htmGAO Y, JI W, XIAO D, et al. Study on the mechanism of "Flos carthami-Semen persicae" on prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease based on network pharmacology[J]. Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med World Sci Technol, 2019, 21(10): 2180-2187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJKX201910025.htm [23] WANG M, LI X S, WANG Z N, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide is associated with long-term mortality risk: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis[J]. Eur Heart J, 2023, 44(18): 1608-1618. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad089 [24] FISCHER K, PRZEPIERA-BEDZAK H, BRZOSKO I, et al. Anti-phosphatidylethanolamine and anti-phosphatidylserine antibodies-Association with renal involvement, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular manifestations, raynaud phenomenon and disease activity in Polish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(10): 1328. doi: 10.3390/biom12101328 [25] NAEINI M B, MOMTAZI-BOROJENI A A, GANJALI S, et al. Phosphatidylserine-containing liposomes: Therapeutic potentials against hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 908: 174308. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174308 [26] CAMONT L, LHOMME M, RACHED F, et al. Small, dense high-density lipoprotein-3 particles are enriched in negatively charged phospholipids: Relevance to cellular cholesterol efflux, antioxidative, antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic functionalities[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2013, 33(12): 2715-2723. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301468 [27] DJUMAGULOV M, DEMESHKINA N, JENNER L, et al. Accuracy mechanism of eukaryotic ribosome translocation[J]. Nature, 2021, 600: 543-546. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04131-9 [28] JIA F Y, WU Q, WANG Z W, et al. BOP1 knockdown attenuates neointimal hyperplasia by activating p53 and inhibiting nascent protein synthesis[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 5986260. [29] SUN H, HUANG X Y, HONG S C. circ0091822 contributes to the proliferation, invasion, and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells under oxidized low-density lipoprotein treatment[J]. Shock, 2023, 60(2): 181-189. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002163 [30] ALTVATER M, SCHUTZ S, CHANG Y M, et al. Dissecting ribosome assembly and transport in budding yeast[J]. Methods Cell Biol, 2014, 122: 437-461. [31] CHEN C, LIU M D, TANG Y T, et al. LncRNA H19 is involved in myocardial ischemic preconditioning via increasing the stability of nucleolin protein[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(9): 5985-5994. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29524 [32] ROSELLO-LLETI E, RIVERA M, CORTE S R, et al. Influence of heart failure on nucleolar organization and protein expression in human hearts[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 418(2): 222-228. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.12.151 [33] DAS S, REDDY M A, SENAPATI P, et al. Diabetes mellitus-induced long noncoding RNA Dnm3os regulates macrophage functions and inflammation via nuclear mechanisms[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2018, 38(8): 1806-1820. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310663 [34] HEIDARY MOGHADDAM R, SAMIMI Z, ASGARY S, et al. Natural AMPK activators in cardiovascular disease prevention[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 12: 738420. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.738420 [35] FENG X J, CHEN W X, NI X Y, et al. Metformin, macrophage dysfunction and atherosclerosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 682853. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.682853 [36] ZHOU X, XU S N, YUAN S T, et al. Multiple functions of autophagy in vascular calcification[J]. Cell Biosci, 2021, 11(1): 159. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00639-9 -





 下载:
下载: