Study on the Enzymatic Deproteinization Technology, Composition Analysis and Immunomodulatory Activity of Isatidis Radix Polysaccharides
-
摘要:
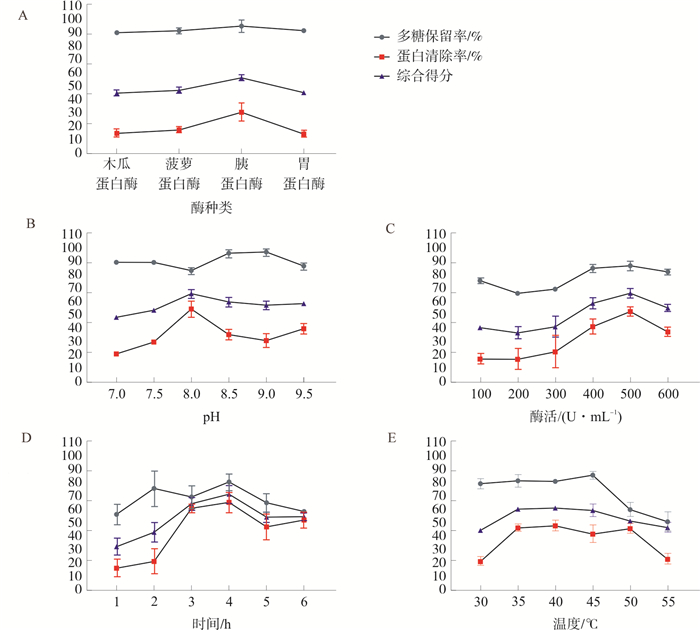
目的 优化板蓝根多糖脱蛋白工艺, 并进一步探讨其免疫调节活性, 为板蓝根多糖的开发利用提供科学依据。 方法 通过单因素结合Box-Behnken响应面法优化酶法脱蛋白的最佳工艺条件; 利用紫外可见光谱、傅里叶变换红外光谱、高效凝胶渗透色谱、高效液相色谱和扫描电镜等方法对板蓝根多糖化学组成与结构特征进行分析; 采用斑马鱼免疫低下模型探讨脱蛋白板蓝根多糖对斑马鱼体内中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞、IL-1β和IL-6含量的影响。 结果 酶法脱蛋白最佳工艺为: 胰蛋白酶500 U·mL-1、pH 8.0、酶解时间5 h、酶解温度37 ℃, 脱蛋白率为(86.39±0.07)%, 综合评分(91.15±0.37)%。紫外、红外光谱扫描和电镜扫描显示酶法可以除去粗多糖中含有的蛋白质, 脱蛋白后相对分子量在5.82~60.26 kDa之间, 单糖摩尔组成为甘露糖∶鼠李糖∶半乳糖醛酸∶葡萄糖∶半乳糖∶阿拉伯糖=2.17∶0.96∶2.90∶83.25∶4.88∶5.84。免疫活性评价结果表明, 脱蛋白后的板蓝根多糖浓度在50~300 μg·mL-1时, 能显著增加斑马鱼免疫细胞密度, 增加巨噬细胞增殖, 降低免疫低下斑马鱼体内IL-1β和IL-6含量, 从而发挥免疫调节作用。 结论 酶法可以有效去除板蓝根粗多糖中的蛋白质, 脱蛋白后的板蓝根多糖具有一定的免疫调节作用。 Abstract:OBJECTIVE To optimize the deproteinization process of Isatidis Radix polysaccharides and further explore its immunomodulatory activity, and to provide a scientific basis for the development and utilization of it. METHODS The optimum conditions of enzymatic deproteinization were optimized by a single factor combined with the Box-Behnken response surface method. The chemical composition and structural characteristics of deproteinized Isatidis Radix polysaccharides were analyzed by UV-visible spectrum, Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy, high-performance gel permeation chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography and scanning electron microscopy. The effects of deproteinized Isatidis Radix Polysaccharide on neutrophils, macrophages, IL-1β and IL-6 in zebrafish were investigated by using a zebrafish immunocompromised model. RESULTS The optimal enzymatic deproteinization process was as follows: trypsin 500 U·mL-1, pH 8.0, enzymatic hydrolysis time 5 h, enzymatic hydrolysis temperature 37 ℃. The deproteinization rate was (86.39±0.07)%, and the comprehensive score was (91.15±0.37)%. Ultraviolet, infrared spectroscopy scanning and scanning electron microscopy showed that the protein contained in the crude polysaccharide could be removed by enzymatic method. The relative molecular weight of the polysaccharides were between 5.82 and 60.26 kDa. The monosaccharide mole composition was mannose∶ rhamnose∶galacturonic acid∶glucose∶galactose∶arabinose=2.17∶0.96∶2.90∶83.25∶4.88∶5.84. The results of immune activity evaluation showed that when the concentration of deproteinized Radix Isatidis polysaccharides was 50~300 μg·mL-1, it could significantly increase the density of zebrafish immune cells, increase the number of macrophages, and reduce the content of IL-1β and IL-6 in immunocompromised zebrafish, thus exerting immunomodulatory effects. CONCLUAION The enzymatic method can effectively remove the proteins contained in the crude polysaccharides of Isatidis Radix, and the deproteinized Isatidis Radix polysaccharides have certain immunomodulatory effects. -
表 1 Box-Behnken实验设计
Table 1. Box-Behnken experimental design
因素 水平 -1 0 1 A(酶活/U) 400 500 600 B(酶解时间/h) 3 4 5 C(pH) 7.5 8.0 8.5 表 2 Box-Behnken响应面实验结果
Table 2. Box-Behnken response surface experiment result
实验号 A(酶活/U·mL-1) B(时间/h) C(pH) 蛋白清除率/% 多糖保留率/% 综合评分 1 400 5 8.0 82.44 76.72 80.15 2 500 5 8.5 67.41 83.15 64.68 3 500 4 8.0 96.79 87.44 93.05 4 500 4 8.0 89.20 81.59 86.15 5 400 4 8.5 34.02 72.34 49.35 6 500 4 8.0 85.82 93.77 89.00 7 500 4 8.0 80.18 93.57 85.54 8 600 4 8.5 44.18 73.02 55.71 9 600 3 8.0 49.95 85.10 78.92 10 600 3 8.0 32.92 79.55 70.95 11 400 4 7.5 62.36 83.83 51.57 12 500 3 7.5 75.13 81.79 77.79 13 600 4 7.5 66.59 97.42 64.01 14 500 3 8.5 76.53 93.18 59.79 15 500 5 7.5 45.58 81.10 83.19 16 600 5 8.0 55.68 78.18 73.71 17 500 4 8.0 87.51 98.54 91.92 表 3 方差分析结果
Table 3. Variance analysis results
变异源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 3 021.91 9 335.77 13.70 0.001 2 significant A(酶活) 51.66 1 51.66 2.11 0.189 9 B(时间) 25.49 1 25.49 1.04 0.341 8 C(pH) 276.48 1 276.48 11.28 0.012 1 * AB 51.91 1 51.91 2.12 0.189 0 AC 9.24 1 9.24 0.38 0.558 7 BC 0.065 1 0.065 0.002 6 0.960 4 A2 909.98 1 909.98 37.12 0.000 5 ** B2 9.49 1 9.49 0.39 0.553 5 C2 1 563.67 1 1563.67 63.78 <0.000 1 ** 残差 171.61 7 24.52 拟失项 126.68 3 42.23 3.76 0.1167 not significant 纯误差 44.94 4 11.23 总和 3 193.52 16 Std.Dev. 4.92 R2 0.946 3 Mean 73.85 Adj R2 0.877 2 C.V.% 6.70 Pred R2 0.343 3 PRESS 2 097.06 信噪比 10.763 0 注:*P<0.05,* *P<0.01。 -
[1] YE D, ZHAO Q, DING D, et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetics-related pharmacological effects of orally administered polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicines: A review[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 252: 126484. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126484 [2] WANG D Y, LIU Y H, ZHAO W. The adjuvant effects on vaccine and the immunomodulatory mechanisms of polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8: 655570. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.655570 [3] ZHAO Y, YAN B C, WANG Z Y, et al. Natural polysaccharides with immunomodulatory activities[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2020, 20(2): 96-106. doi: 10.2174/1389557519666190913151632 [4] YU Y, SHEN M Y, SONG Q Q, et al. Biological activities and pharmaceutical applications of polysaccharide from natural resources: A review[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2018, 183: 91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.009 [5] XIANG X L, LYU J D, DONG M Y, et al. Radix Isatidis polysaccharide (RIP) resists the infection of QX-type infectious bronchitis virus via the MDA5/TLR3/IRF7 signaling pathway[J]. Poult Sci, 2023, 102(4): 102534. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102534 [6] TAO W, FU T, HE Z J, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Radix isatidis polysaccharides in vitro and in vivo[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(6): 1405. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10841 [7] 李海霞, 刘坤璐, 贾培媛, 等. 板蓝根多糖IIP-A-1和IIP-2作为疫苗佐剂的免疫原性[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2019, 33(1): 22-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLBS201901004.htmLI H X, LIU K L, JIA P Y, et al. Immunogenicity of polysaccharides IIP-A-1 and IIP-2 from Isatis indigotica as vaccine adjuvants[J]. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol, 2019, 33(1): 22-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLBS201901004.htm [8] ZENG X T, LI P Y, CHEN X, et al. Effects of deproteinization methods on primary structure and antioxidant activity of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 126: 867-876. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.222 [9] YAN C, BRUNSON D C, TANG Q, et al. Visualizing engrafted human cancer and therapy responses in immunodeficient zebrafish[J]. Cell, 2019, 177(7): 1903-1914. e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.04.004 [10] 李懿, 刘夏进, 宿树兰, 等. 模式生物斑马鱼在中药活性筛选和毒性评价中的应用进展与展望[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2020, 36(5): 715-720. http://xb.njucm.edu.cn/article/id/zr20200522LI Y, LIU X J, SU S L, et al. Application progress and prospect of model organism zebrafish in activity screening and toxicity evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. J Nanjing Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 36(5): 715-720. http://xb.njucm.edu.cn/article/id/zr20200522 [11] 宁奇, 孙培冬, 曹光群, 等. 山药黏液质多糖的酶法脱蛋白工艺及其性能研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2019, 38(9): 118-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXQG201909018.htmNING Q, SUN P D, CAO G Q, et al. Deproteinization technology by enzymic method of polysaccharide from yam mucilage and its performance study[J]. J Food Sci Biotechnol, 2019, 38(9): 118-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXQG201909018.htm [12] 郭庆晖, 张琨霖, 司茜媛, 等. 红甜菜多糖提取条件优化的研究[J]. 中国糖料, 2022, 44(2): 75-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTI202202012.htmGUO Q H, ZHANG K L, SI X Y, et al. Study on optimization of extraction conditions of red beet polysaccharide[J]. Sugar Crops China, 2022, 44(2): 75-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTI202202012.htm [13] LORD J M, MIDWINTER M J, CHEN Y F, et al. The systemic immune response to trauma: An overview of pathophysiology and treatment[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384(9952): 1455-1465. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60687-5 [14] ZENG X T, LI P Y, CHEN X, et al. Effects of deproteinization methods on primary structure and antioxidant activity of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 126: 867-876. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.222 [15] LI M Z, WEN J J, HUANG X J, et al. Interaction between polysaccharides and toll-like receptor 4: Primary structural role, immune balance perspective, and 3D interaction model hypothesis[J]. Food Chem, 2022, 374: 131586. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131586 [16] HOWE K, CLARK M D, TORROJA C F, et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 498-503. doi: 10.1038/nature12111 [17] 孙萌, 王文地, 丽妍, 等. 基于斑马鱼模型的防风多糖调节免疫作用机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(7): 1916-1926. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZY202307025.htmSUN M, WANG W D, LI Y, et al. Immune regulation mechanism of Saposhnikoviae Radix polysaccharide based on zebrafish model[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2023, 48(7): 1916-1926. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZY202307025.htm [18] 张雪, 赵苑伶, 陈林珍, 等. 基于斑马鱼模型探究多花黄精多糖的免疫调节作用[J]. 世界中医药, 2023, 18(6): 761-765, 772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJZA202306001.htmZHANG X, ZHAO Y L, CHEN L Z, et al. Immune function regulation of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua polysaccharides based on zebrafish model[J]. World Chin Med, 2023, 18(6): 761-765, 772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJZA202306001.htm [19] YANG F Q, NAGAHAWATTA D P, YANG H W, et al. In vitro and in vivo immuno-enhancing effect of fucoidan isolated from non-edible brown seaweed Sargassum thunbergii[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 253(Pt 5): 127212. [20] ZHANG N N, MA H, ZHANG Z F, et al. Characterization and immunomodulatory effect of an alkali-extracted galactomannan from Morchella esculenta[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2022, 278: 118960. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118960 -





 下载:
下载: