Research on the Interaction Between Autoimmune Diseases and Gut Microbiota and Regulation of Chinese Herbal Medicines
-
摘要: 自身免疫性疾病是一大类以自身耐受破坏、免疫细胞异常激活、自身抗体产生和大量炎症因子释放, 进而产生多系统损伤为主要特征的疾病。肠道菌群与宿主健康息息相关, 菌群生态失调已被确认与许多自身免疫性疾病的病理生理学有关, 包括类风湿性关节炎、溃疡性结肠炎、自身免疫性甲状腺炎等。中药能改变肠道菌群的组成, 二者之间有紧密联系, 研究发现, 中药可通过重塑肠道微生态结构而发挥治疗作用。该文针对肠道菌群如何影响自身免疫疾病的发生和发展, 结合中药对肠道菌群调节作用的研究, 针对中药调节肠道菌群与其发挥疾病防治效果之间的相关性, 以期为中药的临床应用及药理学研究提供一定的参考依据。Abstract: Autoimmune diseases are characterized as the destruction of self-tolerance, abnormal activation of immune cells, production of autoantibodies and the release of large amounts of inflammatory factors, which in turn result in multisystem damage. The gut microbiota balance is closely related to the host health.Dysbiosis of gut microbiota has been identified in relation to many autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis ulcerative colitis and autoimmune thyroiditis, etc. There has strong relationship between Chinese herbal medicine and its ability to alter the composition of the gut microbiota, and many studies has been proved that Chinese herbal medicine has therapeutic effect by reshaping the intestinal micro-ecological structure. In this review, we aim to investigate how gut microbiota affects the occurrence and development of autoimmune diseases, and to correlate the effects of Chinese herbal medicine on the regulation of gut microbiota with its effectiveness in disease prevention and treatment, with a view to providing a certain reference basis for the clinical application and pharmacological research of Chinese herbal medicine.
-
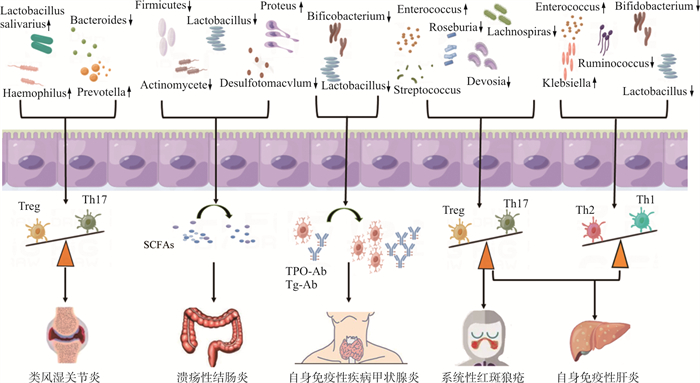
图 1 肠道菌群与自身免疫性疾病关系示意图
注: Haemophilus.嗜血杆菌; Lactobacillus salivarius.唾液乳杆菌; Prevotella.普雷沃氏菌属; Bacteroides.拟杆菌属; Firmicutes.厚壁菌; Actinomycete. 放线菌; Lactobacillus.乳酸杆菌; Desulfotomacvlum.脱硫菌; Proteus.变形杆菌; Bifidobacterium.双歧杆菌; Lachnospira.毛螺菌属; Roseburia.罗氏菌属; Devosia.沃斯菌属; Enterococcus.肠球菌; Streptococcus.链球菌; klebsiella.克雷伯氏菌; Ruminococcus.瘤胃球菌; SCFAs.短链脂肪酸; TPO-Ab.甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体; Tg-Ab.甲状腺球蛋白抗体
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the association between gut microbiota and autoimmune diseases
表 1 中药活性成分调节肠道菌群治疗RA
Table 1. Modulation of gut microbiota by active ingredients in Chinese medicine for RA
中药 菌群变化 相应的指标变化 作用机制 人参皂苷Rg2[17] P. disasonis↑ ZO-1, Occludin↑, LPS↓, Th17↓, Treg↑ 促进P. disasonis的生长, 改变Th17/Treg细胞平衡, 中和致病性自身抗体和改善肠道通透性 朝鲜白术(Nakai)[22] Proteobacteria, Verrucomibia↓
调节Akkermansia、Allobaculum、Anaerovorax、Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002、Lachnoclostridium、Ruminantium_group、Erysipelotricaceae和Muribaculaceae等菌群滑膜浸润和血管增殖减轻, TNF-α、IL-1、IL-1β、IL-2、IL-6、hs-CRP水平↓ 可能与下调炎症因子、改善肠道菌群和SCFAs平衡有关 棘球蚴总多糖和糖苷[23] Proteobacteria、Acidobacteria和Gemmatimonadetes↑, Tenericutes、Fusobacteria、Kiritimatiellaeota和Patescibacteria↓ 抑制关节炎, 血清中IL-1β和TNF-α↓ 可能是通过调节肠道菌群来调节代谢产物的产生 紫檀芪[24] Helicobacter、Desulfovibrio、Lachnospiraceae和Mucispirillium↓ MPO、IgG1、IgG2A、TNF-α、COX-2、NF-κB↓, IL-10↑ 通过降低炎症因子和介质的水平显著抑制炎症 鸡矢藤提取物[25] Desulfotomacvlum、Spirochaete、Mucilaginosa、Helicobacterpylori和Lachnospiraceae↓ TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6、IL-7和IL-23↓ 直接抑制循环血液中促炎细胞因子和介质的产生 铁总线莲三萜皂苷[26] Firmicutes和Actinobacteria的G-细菌↓, G+细菌↑, 达到G-/G+比率平衡 总SCFAs↓ 可能通过平衡肠道微生物群和SCFAs代谢来缓解DMARDs的胃肠道损害副作用 当归四逆汤[27] g-Norank-f-Eubacterium-coprostanoligenes-group和g-Lactobacillus↓, g-Bacteroides↑ 滑膜浸润和血管增殖减轻, SCFAs↓ 通过影响肠道微生物群及其代谢物 表 2 中药活性成分调节肠道菌群治疗UC
Table 2. Modulation of gut microbiota by active ingredients in Chinese medicine for UC
中药成分 菌群变化 相应的指标变化 作用机制 白头翁皂苷[37] norank_F_Muribaculaceae和norank_F_norank_O_Clostridia_UCG-014↑, 有害拟杆菌↓ 结肠黏膜结构和病理炎症改善 可能与有益菌的显著增加以及有害菌的减少有关 柴胡皂苷-d[38] Lachnospiraceae、Ruminiclostridium_5、Mucispirillum、Ruminiclostridium_9、Ruminiclostridium、Oscillibacter、Blautia和Anaerotruncus↑, Ruminiclostridium-6↓ 结肠病理炎症改善, IL-10、ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-1↑, IL-6、IL-8、IL-1β、TNF-α↓ 通过抑制NF-κB活化和调节小鼠肠道微生物群来改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的结肠炎 地黄多糖[39] Firmicutes和Lactobacillus↑, Bacteroides↓ IL-10、ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-1↑, IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α↓, 抑制NF-κB通路 可能通过恢复紊乱的肠道微生物组和微生物群落代谢物来介导, 从而增强肠上皮屏障, 增强紧密连接蛋白的表达, 并通过NF-κB途径抑制促炎因子的过表达 雷公藤[40] Bacteroides和Lachnospiraceae↓ 结肠病理炎症减轻, IL-6、IL-17和TNF-α↓ 可能与通过改善肠道菌群结构, 恢复细菌多样性, 来调节肠道菌群有关 人参皂苷Rg1[41] Lachnospiraceae↑, Staphylococcus、Bacteroide和Ruminococcaceae_UCG_014↓ 结肠病理炎症改善, IL-4、IL-10↑, IL-6、IL-33、TNF-α、Rock1、RhoA和Nogo-B蛋白↓ 调节炎性细胞因子表达; 抑制巨噬细胞活化; 调节M1/M2巨噬细胞极化平衡并改善肠道菌群; 抑制结肠炎小Nogo-B/RhoA信号通路激活等 淫羊藿苷[42] Helicobacteraceae、Bacteroides和Tricibacter↓, Lachnospiraceae、Akkermansia和Lactobacillus↑ 结肠病理结构改善, 结肠长度延长, IL-6、TNF-α↓, 抑制NF-κB通路 通过调节p-p65/p65表达, 提高肠道菌群丰度和组成, 抑制组织损伤和炎症反应 黄芪素[43] Ruminiclostridium_9, Oscillibacter, Butyricicoccus, Ruminiclostridium, Ruminococcaceae_NK4A214_group, and Ruminococcaceae_UCG-009↑ ZO-1和Occludin↑, TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6↓, 抑制NF-κB通路 抑制促炎细胞因子和NF-κB信号通路的活化, 改善肠道屏障功能和代谢内毒素血症, 并部分逆转UC小鼠肠道微生物群的改变 丹参酸A[44] Akkermansia、Bacillus、Blautia、Lachnoclostridium和Lactobacillus↑, Bacteroides、Roseburia和Ruminiclostridium↓ 结肠病理炎症改善, ZO-1、TGF-β↑, IL-1β、IL-6、MCP-1↓ 对炎症介质的调节, 利于肠道菌群的稳定, 通过选择性地促进益生菌的生长 雪积草苷[45] Helicobacter、Jeotgalicoccus和Staphylococcus↓ 结肠病理炎症改善, ZO-1、E-cadherin表达↑ 可能依赖于黏膜屏障和肠道微生物群稳态的恢复 苦豆子总碱[46] Desulfovibrio、Corynebacterium和Adlercreutzia↑, Mucispirillum和Butyricimonas↓ IL-1β、TGF-β1、血清TBA、T-CHO↓,IL-10↑ 减轻结肠损伤, 调节肠道微生物群的平衡和胆汁酸代谢 表 3 中药活性成分调节肠道菌群治疗AIT
Table 3. Modulation of gut microbiota by active ingredients in Chinese medicine for AIT
中药成分 菌群变化 相应的指标变化 作用机制 芪箭消瘿方[52] Lactobacillus↑(中、低剂量)Prevotellaceae↓(中、高剂量) sIgA、ZO-1和Occludin↑ 可能与调节肠道菌群生物多样性及物种组成有关, 进而增加结肠紧密连接蛋白及sIgA表达 软坚消瘿颗粒[53] Firmicutes、Clostridium、Clostridiales、Ruminococcaceae和Prevotella↓, Proteobacteria、Moraxoniaceae、Alphaproteobacteria、Escherichia和Myroides↑ TGAb和TPoAb↓, TSH↑ 影响代谢产物和代谢通路, 调节肠道菌群有关 白芍总苷[54] Lactobacillus、Prevotellaceae和Romboutsia↑ 甲状腺病变程度减轻, TG-Ab、TPO-Ab和TNF-α↓, IL-10、sIgA、ZO-1和Occludin蛋白↑ 可能通过调节肠道菌群组成及多样性, 改善肠黏膜屏障损伤从而发挥治疗AIT的作用 益气化痰活血方[55] Firmicutes和F/B↓, Bacteroidetes和Actinobacteria↑ 血清TG-Ab↓,减轻甲状腺淋巴细胞炎症浸润程度 可能与改变肠道菌群的结构及组成有关 -
[1] HOOPER LV, MACPHERSON AJ. Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2010, 10(3): 159-169. doi: 10.1038/nri2710 [2] ADAK A, KHAN MR. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(3): 473-493. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2943-4 [3] SÁNCHEZ-TAPIA M, TOVAR AR, TORRES N. Diet as regulator of gut microbiota and its role in health and disease[J]. Arch Med Res, 2019, 50(5): 259-268. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2019.09.004 [4] KAU AL, AHERN PP, GRIFFIN NW, et al. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system[J]. Nature, 2011, 474(7351): 327-336. doi: 10.1038/nature10213 [5] SHEN HK, ZHAO ZT, ZHAO ZJ, et al. Native and engineered probiotics: Promising agents against related systemic and intestinal diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(2): 594. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020594 [6] ZHANG X, CHEN BD, ZHAO LD, et al. The gut microbiota: Emerging evidence in autoimmune diseases[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2020, 26(9): 862-873. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2020.04.001 [7] 方心宇, 冷瑞雪, 范引光, 等. 自身免疫性疾病流行病学研究进展[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(8): 869-873. doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.08.001FANG XY, LENG RX, FAN YG, et al. Research advances in the epidemiology of autoimmune diseases[J]. Chin J Dis Contr Prev, 2021, 25(8): 869-873. doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.08.001 [8] DANIELI MG, ANTONELLI E, PIGA MA, et al. Alarmins in autoimmune diseases[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2022, 21(9): 103142. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2022.103142 [9] FUGGER L, JENSEN LT, ROSSJOHN J. Challenges, progress, and prospects of developing therapies to treat autoimmune diseases[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(1): 63-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.007 [10] SAURIN S, MEINECK M, ERKEL G, et al. Drug candidates for autoimmune diseases[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2022, 15(5): 503. doi: 10.3390/ph15050503 [11] 赵丽丹, 孟夏, 徐浩杰, 等. 肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病治疗中的前景[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2022, 13(5): 740-746. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XHYX202205005.htmZHAO LD, MENG X, XU HJ, et al. Prospect of gut microbiota-based intervention in autoimmune disease control[J]. Med J Peking Union Med Coll Hosp, 2022, 13(5): 740-746. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XHYX202205005.htm [12] LU C, XU K, GUO H. The relationship of PADI4_94 polymorphisms with the morbidity of rheumatoid arthritis in Caucasian and Asian populations: A meta-analysis and system review[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2018, 37(2): 289-296. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3964-3 [13] 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 2018中国类风湿关节炎诊疗指南[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2018, 57(4): 242-251. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2018.04.004Chinese Rheumatology Association. 2018 Chinese guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2018, 57(4): 242-251. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2018.04.004 [14] NOACK M, MIOSSEC P. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2014, 13(6): 668-677. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.12.004 [15] VAGHEF-MEHRABANY E, ALIPOUR B, HOMAYOUNI-RAD A, et al. Probiotic supplementation improves inflammatory status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Nutrition, 2014, 30(4): 430-435. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2013.09.007 [16] FAN ZX, ROSS RP, STANTON C, et al. Lactobacillus casei CCFM1074 alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in rats via balancing Treg/Th17 and modulating the metabolites and gut microbiota[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 680073. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.680073 [17] SUN HJ, GUO YK, WANG HD, et al. Gut commensal Parabacteroides distasonis alleviates inflammatory arthritis[J]. Gut, 2023, 2023: 327756. [18] ZHANG X, ZHANG DY, JIA HJ, et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment[J]. Nat Med, 2015, 21(8): 895-905. doi: 10.1038/nm.3914 [19] SCHER JU, SCZESNAK A, LONGMAN RS, et al. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis[J]. eLife, 2013, 2: e01202. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01202 [20] HASAN H, ISMAIL H, EL-ORFALI Y, et al. Therapeutic benefits of Indole-3-Carbinol in adjuvant-induced arthritis and its protective effect against methotrexate induced-hepatic toxicity[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2018, 18(1): 337. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2408-1 [21] SHIRANI K, IRANSHAHI M, ASKARI VR, et al. Comparative evaluation of the protective effects of oral administration of auraptene and umbelliprenin against CFA-induced chronic inflammation with polyarthritis in rats[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 139: 111635. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111635 [22] PANG J, MA SP, XU XY, et al. Effects of rhizome of Atractylodes koreana (Nakai) Kitam on intestinal flora and metabolites in rats with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 281: 114026. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114026 [23] LI YZ, DAI MX, WANG LL, et al. Polysaccharides and glycosides from Aralia echinocaulis protect rats from arthritis by modulating the gut microbiota composition[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 269: 113749. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113749 [24] RUI Z, ZHANG L, LI XF, et al. Pterostilbene exert an anti-arthritic effect by attenuating inflammation, oxidative stress, and alteration of gut microbiota[J]. J Food Biochem, 2022, 46(5): e14011. [25] XIAO M, FU XP, NI YL, et al. Protective effects of Paederia scandens extract on rheumatoid arthritis mouse model by modulating gut microbiota[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 226: 97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.012 [26] GUO LX, WANG HY, LIU XD, et al. Saponins from Clematis mandshurica Rupr. regulates gut microbiota and its metabolites during alleviation of collagen-induced arthritis in rats[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 149: 104459. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104459 [27] HE Y, CHENG B, GUO BJ, et al. Metabonomics and 16S rRNA gene sequencing to study the therapeutic mechanism of Danggui Sini Decoction on collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis rats with Cold Bi syndrome[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2023, 222: 115109. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.115109 [28] ALTOMARE A, PUTIGNANI L, DEL CHIERICO F, et al. Gut mucosal-associated microbiota better discloses inflammatory bowel disease differential patterns than faecal microbiota[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2019, 51(5): 648-656. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.11.021 [29] BARYSHNIKOVA N, USPENSKIY Y, SUVOROVA M, et al. P690 Changes of intestinal microbiota in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2021, 15(Supplement_1): S607. [30] TAKAHASHI K, NISHIDA A, FUJIMOTO T, et al. Reduced abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria species in the fecal microbial community in Crohn ' s disease[J]. Digestion, 2016, 93(1): 59-65. doi: 10.1159/000441768 [31] YAO Y, CAI XY, FEI WD, et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in immunity, inflammation and metabolism[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2022, 62(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1854675 [32] ATARASHI K, TANOUE T, OSHIMA K, et al. Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of Clostridia strains from the human microbiota[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7461): 232-236. doi: 10.1038/nature12331 [33] SINGH SB, COFFMAN CN, CARROLL-PORTILLO A, et al. Notch signaling pathway is activated by sulfate reducing bacteria[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 695299. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.695299 [34] ROWAN F, DOCHERTY NG, MURPHY M, et al. Desulfovibrio bacterial species are increased in ulcerative colitis[J]. Dis Colon Rectum, 2010, 53(11): 1530-1536. doi: 10.1007/DCR.0b013e3181f1e620 [35] INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE GROUP CSOG. Chinese consensus on diagnosis and treatment in inflammatory bowel disease (2018, Beijing)[J]. J Dig Dis, 2021, 22(6): 298-317. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12994 [36] NAKASE H, UCHINO M, SHINZAKI S, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for inflammatory bowel disease 2020[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2021, 56(6): 489-526. doi: 10.1007/s00535-021-01784-1 [37] LIU YL, ZHOU MY, YANG M, et al. Pulsatilla chinensis saponins ameliorate inflammation and DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by regulating the composition and diversity of intestinal flora[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 728929. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.728929 [38] LI PZ, WU MN, XIONG WC, et al. Saikosaponin-d ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by suppressing NF-κB activation and modulating the gut microbiota in mice[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 81: 106288. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106288 [39] LV H, JIA HP, CAI WJ, et al. Rehmannia glutinosa polysaccharides attenuates colitis via reshaping gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid production[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2023, 103(8): 3926-3938. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12326 [40] WU H, RAO Q, MA GC, et al. Effect of triptolide on dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis and gut microbiota in mice[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 10: 1652. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01652 [41] LONG J, LIU XK, KANG ZP, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorated experimental colitis by regulating the balance of M1/M2 macrophage polarization and the homeostasis of intestinal flora[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2022, 917: 174742. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174742 [42] ZHANG HR, ZHUO SX, SONG DN, et al. Icariin inhibits intestinal inflammation of DSS-induced colitis mice through modulating intestinal flora abundance and modulating p-p65/p65 molecule[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2021, 32(4): 382-392. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2021.20282 [43] PENG L, GAO XY, NIE L, et al. Astragalin attenuates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced acute experimental colitis by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis and inhibiting NF-κB activation in mice[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 2058. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02058 [44] WANG K, YANG QQ, MA QX, et al. Protective effects of salvianolic acid A against dextran sodium sulfate-induced acute colitis in rats[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(6): 791. doi: 10.3390/nu10060791 [45] LI HB, CHEN XH, LIU JY, et al. Ethanol extract of Centella asiatica alleviated dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis: Restoration on mucosa barrier and gut microbiota homeostasis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 267: 113445. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113445 [46] JIA YQ, YUAN ZW, ZHANG XS, et al. Total alkaloids of Sophora alopecuroides L. ameliorated murine colitis by regulating bile acid metabolism and gut microbiota[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 255: 112775. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112775 [47] LEE DSW, ROJAS OL, GOMMERMAN JL. B cell depletion therapies in autoimmune disease: Advances and mechanistic insights[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2021, 20(3): 179-199. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-00092-2 [48] DWIVEDI SN, KALARIA T, BUCH H. Thyroid autoantibodies[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2023, 76(1): 19-28. doi: 10.1136/jcp-2022-208290 [49] BRČIĆ L, BARIĆ AN, GRAČAN S, et al. Association of established thyroid peroxidase autoantibody (TPOAb) genetic variants with Hashimoto ' s thyroiditis[J]. Autoimmunity, 2016, 49(7): 480-485. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2016.1191475 [50] GONG BS, WANG CY, MENG FR, et al. Association between gut microbiota and autoimmune thyroid disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2021, 12: 774362. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.774362 [51] KNEZEVIC J, STARCHL C, TMAVA BERISHA A, et al. Thyroid-gut-axis: How does the microbiota influence thyroid function?[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(6): 1769. doi: 10.3390/nu12061769 [52] 牧亚峰, 左新河, 向楠, 等. 基于"肠道菌群-黏膜屏障"探讨芪箭消瘿方对自身免疫性甲状腺炎大鼠的作用机制研究[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2022, 28(3): 362-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYJC202203014.htmMU YF, ZUO XH, XIANG N, et al. Study on mechanism of Qijian Xiaoying recipe on autoimmune thyroiditis rats based on intestinal flora mucosal barrier[J]. J Basic Chin Med, 2022, 28(3): 362-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYJC202203014.htm [53] 董天娇. 基于代谢组学及肠道菌群探讨软坚消瘿颗粒对EAT大鼠的作用机制[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁中医药大学, 2022.DONG TJ. Based on metabonomics and intestinal flora, the mechanism of Ruanjian Xiaoying Granule on EAT rats was discussed[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022. [54] 牧亚峰, 向楠, 左新河, 等. 白芍总苷对自身免疫性甲状腺炎大鼠肠黏膜屏障及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(11): 3269-3277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO202111014.htmMU YF, XIANG N, ZUO XH, et al. Effects of total glucosides of Paeonia lactiflora on intestinal mucosal barrier and intestinal flora in rats with autoimmune thyroiditis[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2021, 52(11): 3269-3277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO202111014.htm [55] 郭风宜, 刘子玉, 王智民, 等. 益气化痰活血方对自身免疫性甲状腺炎小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2023, 34(2): 292-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZGY202302010.htmGUO FY, LIU ZY, WANG ZM, et al. Effect of Yiqi Huatan Huoxue recipe on intestinal flora in mice with autoimmune thyroiditis[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2023, 34(2): 292-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZGY202302010.htm [56] ZHANG SW, GANG XK, YANG S, et al. The alterations in and the role of the Th17/treg balance in metabolic diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 678355. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.678355 [57] LI D, GUO B, WU HJ, et al. Interleukin-17 in systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive review[J]. Autoimmunity, 2015, 48(6): 353-361. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1037441 [58] ZHANG MX, YIN XF. AB0137 diversity analysis of intestinal flora in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020, 79: 1369. [59] ZHANG LL, WEI W. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of paeoniflorin and total glucosides of paeony[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 207: 107452. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107452 [60] ZHAO X, TANG XJ, YAN Q, et al. Triptolide ameliorates lupus via the induction of miR-125a-5p mediating Treg upregulation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 71: 14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.02.047 [61] MOMTAZI-BOROJENI AA, HAFTCHESHMEH SM, ESMAEILI SA, et al. Curcumin: A natural modulator of immune cells in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2018, 17(2): 125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.11.016 [62] LIAO JY, LIU Y, WU HJ, et al. The role of icaritin in regulating Foxp3/IL17a balance in systemic lupus erythematosus and its effects on the treatment of MRL/lpr mice[J]. Clin Immunol, 2016, 162: 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.11.006 [63] 王维钊, 向晓星. Treg/Th17、Th1/Th2平衡在自身免疫性肝炎中的免疫学机制及诊疗新靶点[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(8): 1874-1877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.051WANG WZ, XIANG XX. Immunological mechanism of Treg/Th17 and Th1/Th2 balance in autoimmune hepatitis and new targets for diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(8): 1874-1877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.051 [64] LIU YL, YAN WM, YUAN W, et al. Treg/Th17 imbalance is associated with poor autoimmune hepatitis prognosis[J]. Clin Immunol, 2019, 198: 79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2018.11.003 [65] MANFREDO VIEIRA S, HILTENSPERGER M, KUMAR V, et al. Translocation of a gut pathobiont drives autoimmunity in mice and humans[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6380): 1156-1161. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7201 [66] LIU QY, HE W, TANG RQ, et al. Intestinal homeostasis in autoimmune liver diseases[J]. Chin Med J, 2022, 135(14): 1642-1652. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002291 [67] ZHU LR, LI SS, ZHENG WQ, et al. Targeted modulation of gut microbiota by traditional Chinese medicine and natural products for liver disease therapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1086078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1086078 -





 下载:
下载: