XingNaoJing Alleviated Adult Mice Cognitive Dysfunction Induced by Sevoflurane through Inhibition of the Notch Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:
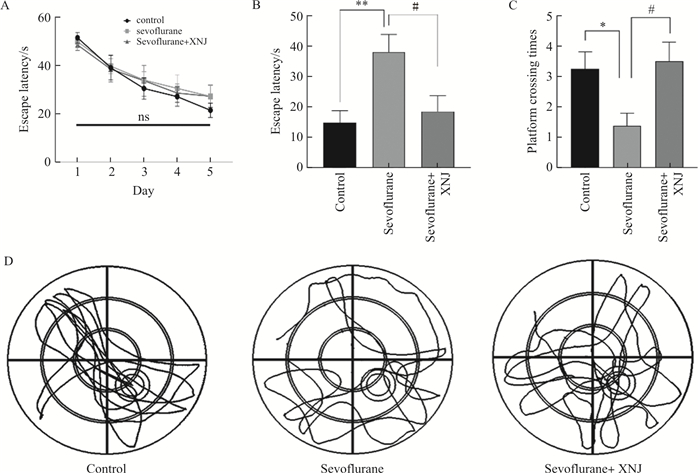
目的 探究醒脑静注射液减轻七氟烷引起认知障碍的机制及Notch信号通路的相关作用。 方法 将36只8~12周龄的SPF级雄性C57BL/6J小鼠随机分成3组: 对照组、七氟烷组以及七氟烷+醒脑静组,每组12只。Morris水迷宫检测各组小鼠认知行为能力; 免疫荧光及qPCR技术检测各组小鼠的海马炎症水平; 免疫荧光检测各组小鼠海马神经干细胞的增殖功能; Western blot检测Notch信号通路相关蛋白的表达。 结果 Morris水迷宫表明吸入3%浓度七氟烷6 h可导致成年小鼠认知功能损伤。免疫荧光实验表明吸入七氟烷后海马小胶质细胞被激活, 神经干细胞增殖功能被抑制; qPCR及Western blot实验表明七氟烷能增加M1型促炎性细胞因子mRNA水平以及Notch信号通路相关蛋白的表达。 结论 醒脑静注射液通过调节Notch信号通路减轻七氟烷诱导的学习记忆障碍,提示醒脑静注射液预处理可能是预防七氟烷致成年小鼠术后认知障碍的可行措施。 Abstract:OBJECTIVE To explore XingNaoJing injection how to alleviated postoperative cognitive dysfunction induced by sevoflurane and the Notch signaling pathway potential effect during above process. METHODS 36 male C57BL/6J mice aged of 8-12 weeks were randomly divided into three groups: control (Con), Sevoflurane (Sev), and sevoflurane+XingNaoJing injection(Sev+XNJ) groups, with 12 mice in each group. The cognitive abilities of mice in each group were tested using the Morris water maze. The hippocampal inflammation level in each group were tested using the immunofluorescence and qPCR. The neural stem cells proliferation function in each group were tested using the immunofluorescence. The relative protein expression of the Notch signaling pathway in each group were tested using the Western blotting. RESULTS The Morris water maze results showed that 3% sevoflurane exposure for 6 hours induced cognitive dysfunction in adult mice. Immunofluorescence results showed that hippocampal microglia were activated and neural stem cells proliferation was inhibited. qPCR and Western blot analysis showed that the mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the expression level of the Notch signaling pathway-related proteins in the hippocampus were upregulated by sevoflurane. CONCLUSION XingNaoJing injection mitigated sevoflurane-induced deficits in learning and memory by modulating the Notch signaling pathway. This research raised the possibility that XingNaoJing injection pretreatment might be a feasible measure to prevent postoperative cognitive deficits in adult mice induced by sevoflurane. -
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer Sequences
引物 正向(5'-3') 反向(5'-3') TNF-α TTCTCATTCCTGCTTGTGG ACTTGGTGGTTTGCTACG IL-6 CCACCAAGAACGATAGTCAA TTTCCACGATTTCCCAGA IL-12 p35 GGACCAAACCAGCACAT CGCAGAGTCTCGCCATTA GAPDH TGCGACTTCAACAGCAACTC CTTGCTCAGTGTCCTTGCTG -
[1] WANG CM, CHEN WC, ZHANG Y, et al. Update on the mechanism and treatment of sevoflurane-induced postoperative cognitive dysfunction[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2021, 13: 702231. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.702231 [2] CUI RS, WANG K, WANG ZL. Sevoflurane anesthesia alters cognitive function by activating inflammation and cell death in rats[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15(5): 4127-4130. [3] GARRONE B, DURANDO L, PRENDERVILLE J, et al. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) rescues cognitive decline, neuroinflammation and cytoskeletal alterations in a model of post-operative cognitive decline (POCD) in middle-aged rats[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 10139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89629-y [4] SHAO AM, FEI JP, FENG SQ, et al. Chikusetsu saponin IVa alleviated sevoflurane-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment by blocking NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2020, 72(4): 833-845. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00078-2 [5] DONG P, ZHAO J, LI N, et al. Sevoflurane exaggerates cognitive decline in a rat model of chronic intermittent hypoxia by aggravating microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via downregulation of PPAR-γ in the hippocampus[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2018, 347: 325-331. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.03.031 [6] XU X, ZHAO Y, XU MZ, et al. Activation of Notch signal pathway is associated with a poorer prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Med Oncol, 2011, 28(1): 483-489. [7] REN SG, ZHANG XM, HU YY, et al. Blocking the Notch signal transduction pathway promotes tumor growth in osteosarcoma by affecting polarization of TAM to M2 phenotype[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(17): 1057. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3881 [8] SUN QS, LUO M, ZHAO HM, et al. Overexpression of PKMYT1 indicates the poor prognosis and enhances proliferation and tumorigenesis in non-small cell lung cancer via activation of Notch signal pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(10): 4210-4219. [9] LIU ZB, TANG C, JIN X, et al. Increased expression of lncRNA SNHG12 predicts a poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and regulates cell proliferation and metastasis by modulating Notch signal pathway[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2018, 23(4): 603-613. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181873 [10] TINDEMANS I, VAN SCHOONHOVEN A, KLEINJAN A, et al. Notch signaling licenses allergic airway inflammation by promoting Th2 cell lymph node egress[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(7): 3576-3591. doi: 10.1172/JCI128310 [11] LAVOZ C, POVEDA J, MARQUEZ-EXPOSITO L, et al. Gremlin activates the Notch pathway linked to renal inflammation[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2018, 132(11): 1097-1115. doi: 10.1042/CS20171553 [12] TODA T, PARYLAK SL, LINKER SB, et al. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2019, 24(1): 67-87. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0036-2 [13] OLABIYI BF, FLEITAS C, ZAMMOU B, et al. proNGF involvement in the adult neurogenesis dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10744. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910744 [14] TODA T, GAGE FH. Adult neurogenesis contributes to hippocampal plasticity[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2018, 373(3): 693-709. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2735-4 [15] KHEIRBEK MA, HEN R. (Radio)active neurogenesis in the human Hippocampus[J]. Cell, 2013, 153(6): 1183-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.033 [16] SANAI N, NGUYEN T, IHRIE RA, et al. Corridors of migrating neurons in the human brain and their decline during infancy[J]. Nature, 2011, 478(7369): 382-386. doi: 10.1038/nature10487 [17] SPALDING KL, BERGMANN O, ALKASS K, et al. Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans[J]. Cell, 2013, 153(6): 1219-1227. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.002 [18] VALERO J, BERNARDINO L, CARDOSO FL, et al. Impact of neuroinflammation on hippocampal neurogenesis: Relevance to aging and Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2017, 60(S1): S161-S168. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170239 [19] ZHANG YM, QU XY, TAO LN, et al. XingNaoJing injection ameliorates cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury via SIRT1-mediated inflammatory response inhibition[J]. Pharm Biol, 2020, 58(1): 16-24. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1698619 [20] ZHANG YM, QU XY, ZHAI JH, et al. Xingnaojing injection protects against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt-mediated eNOS phosphorylation[J]. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med, 2018, 2018: 2361046. [21] MA X, YANG YX, CHEN N, et al. Meta-analysis for clinical evaluation of Xingnaojing injection for the treatment of cerebral infarction[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 485. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00485 [22] 薛冰心, 张邓新, 邱丽颖, 等. 醒脑静对七氟烷麻醉小鼠海马中突触结合蛋白-Ⅰ表达的影响与学习记忆相关性[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2016, 32(6): 162-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYL201606045.htmXUE BX, ZHANG DX, QIU LY, et al. Effect of Xingnaojing on the expression of synaptotagmin-Ⅰin hippocampus of mice with sevoflurane anesthesia and ability of learning and memory in mice[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2016, 32(6): 162-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYL201606045.htm [23] ZHANG DX, XUE BX, YOU J, et al. Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid reversed cognitive and synaptic plasticity impairments induced by sevoflurane exposure in adult mice[J]. Neuroreport, 2019, 30(4): 274-279. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001196 [24] KOTEKAR N, SHENKAR A, NAGARAJ R. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction-current preventive strategies[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2018, 13: 2267-2273. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S133896 [25] NIE Y, WANG Z, CHAI G, et al. Dehydrocostus lactone suppresses LPS-induced acute lung injury and macrophage activation through NF-κB signaling pathway mediated by p38 MAPK and Akt[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(8): E1510. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081510 [26] JIANG M, TANG TX, LIANG XY, et al. Maternal sevoflurane exposure induces temporary defects in interkinetic nuclear migration of radial glial progenitors in the fetal cerebral cortex through the Notch signalling pathway[J]. Cell Prolif, 2021, 54(6): e13042. [27] FEI X, WANG JX, WU Y, et al. Sevoflurane-induced cognitive decline in aged mice: Involvement of toll-like receptors 4[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2020, 165: 23-29. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.08.030 [28] ZHAO LL, GONG HX, HUANG HJ, et al. Participation of mind bomb-2 in sevoflurane anesthesia induces cognitive impairment in aged mice via modulating ferroptosis[J]. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2021, 12(13): 2399-2408. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00131 [29] LIANG R, OU SS, HAN YX, et al. Plasma amyloid beta level changes in aged mice with cognitive dysfunction following sevoflurane exposure[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2020, 129: 110737. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2019.110737 [30] WANG XN, DONG YL, ZHANG YY, et al. Sevoflurane induces cognitive impairment in young mice via autophagy[J]. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14(5): e0216372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216372 [31] LIU MY, SONG SY, CHEN QC, et al. Gut microbiota mediates cognitive impairment in young mice after multiple neonatal exposures to sevoflurane[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(12): 16733-16748. doi: 10.18632/aging.203193 [32] TANG XL, ZHAO YL, ZHOU ZQ, et al. Resveratrol mitigates sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity by the SIRT1-dependent regulation of BDNF expression in developing mice[J]. Oxidative Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 9018624. [33] YIN J, ZHAO X, WANG LJ, et al. Sevoflurane-induced inflammation development: Involvement of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway[J]. Behav Pharmacol, 2019, 30(8): 730-737. [34] YANG ZY, YUAN CX. IL-17A promotes the neuroinflammation and cognitive function in sevoflurane anesthetized aged rats via activation of NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2018, 18(1): 147. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0607-4 [35] LV GY, LI CG, WANG WW, et al. Silencing SP1 alleviated sevoflurane-induced POCD development via cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway[J]. Neurochem Res, 2020, 45(9): 2082-2090. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03070-7 [36] TIAN Y, GUO SB, MA L, et al. Sevoflurane aggregates cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal oxidative stress induced by β-amyloid in rats[J]. Life Sci, 2015, 143: 194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.11.002 [37] ZHANG XM, ZHOU YF, XU MM, et al. Autophagy is involved in the sevoflurane anesthesia-induced cognitive dysfunction of aged rats[J]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 11(4): e0153505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153505 [38] GE X, ZUO Y, XIE JH, et al. A new mechanism of POCD caused by sevoflurane in mice: Cognitive impairment induced by cross-dysfunction of iron and glucose metabolism[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(18): 22375-22389. doi: 10.18632/aging.203544 [39] HOSSAIN MM, BELKADI A, AL-HADDAD S, et al. Deltamethrin exposure inhibits adult hippocampal neurogenesis and causes deficits in learning and memory in mice[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2020, 178(2): 347-357. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa144 [40] BABCOCK KR, PAGE JS, FALLON JR, et al. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in aging and Alzheimer's disease[J]. Stem Cell Rep, 2021, 16(4): 681-693. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.01.019 [41] KIM IB, PARK SC. The entorhinal cortex and adult neurogenesis in major depression[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(21): 11725. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111725 [42] PARK SC. Neurogenesis and antidepressant action[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2019, 377(1): 95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00441-019-03043-5 [43] TANG MM, LIN WJ, ZHANG JT, et al. Exogenous FGF2 reverses depressive-like behaviors and restores the suppressed FGF2-ERK1/2 signaling and the impaired hippocampal neurogenesis induced by neuroinflammation[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2017, 66: 322-331. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.05.013 [44] OSMAN AM, RODHE J, SHEN XL, et al. The secretome of microglia regulate neural stem cell function[J]. Neuroscience, 2019, 405: 92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.10.034 [45] SIEBEL C, LENDAHL U. Notch signaling in development, tissue homeostasis, and disease[J]. Physiol Rev, 2017, 97(4): 1235-1294. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00005.2017 [46] KOPAN R, ILAGAN MXG. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(2): 216-233. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.045 [47] QIAN DF, LI LW, RONG YL, et al. Blocking Notch signal pathway suppresses the activation of neurotoxic A1 astrocytes after spinal cord injury[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(21): 3010-3029. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1667189 [48] WU L, LI YS, YU MH, et al. Notch signaling regulates microglial activation and inflammatory reactions in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy[J]. Neurochem Res, 2018, 43(6): 1269-1282. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2544-5 [49] QU XY, ZHANG YM, TAO LN, et al. XingNaoJing injections protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and alleviate blood-brain barrier disruption in rats, through an underlying mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasomes suppression[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2019, 17(7): 498-505. -





 下载:
下载: