Research Progress of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Marine Natural Products
-
摘要: α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂(α-Glucosidase inhibitors,AGIs)是一类通过减少葡萄糖在肠道的吸收而降低餐后血糖的新型抗糖尿病药物。AGIs降糖平稳、安全性高,并可降低心血管并发症的发生率。但是上市AGIs药物数量较少,且均具有一定副作用,使得开发新型AGIs具有重要意义。海洋天然产物作为药物开发的重要宝库,是寻找开发新型AGIs的重要方向。该文综述了59个来源于海洋动物、藻类和微生物的天然AGIs,对他们的化合物类型和活性进行了介绍,为从海洋天然产物中开发新型高效的AGIs提供参考。
-
关键词:
- α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂 /
- 糖尿病 /
- 海洋天然产物
Abstract: The α-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs) are a kind of new antidiabetic drugs that can slow down the absorption of glucose in the intestinal tract and reduce postprandial blood glucose. AGIs can stabilize and gradually maintain blood glucose at a certain level without inducing complications. However, the number of AGIs drugs on the market is small and all of them have certain side effects, which makes it of great significance to develop new AGIs. As an important source of drug development, the marine natural product is an important way to find new AGIs. In this paper, natural AGIs from 59 marine animals, algae and microorganisms were reviewed to provide references for the development of new safe and efficient AGIs from marine natural products.-
Key words:
- α-glucosidase inhibitors /
- diabetes mellitus /
- marine natural products
-
表 1 海洋动物来源的AGIs
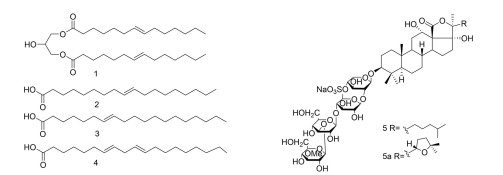
化合物 海洋动物 化合物来源 AGIs IC50 化合物种类 参考文献 1 海参 Tichopus japonicus 甘油二棕榈油酸酯(1, 3-Dipalmitolein) 4.45 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 脂肪酸 10 2 顺式-9-十八碳烯酸(Cis-9-Octadecenoic acid) 14.87 μmol·L-1(嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌) 9 3 7Z-十八碳二烯酸(7Z-Octadecenoic acid) 0.005 1 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 4 7Z,10Z-十八碳二烯酸(7Z, 10Z-Octadecadienoic acid) 0.000 49 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 0.000 6 g·L-1(嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌) 5 Pearsonothuria graeffei 海参皂苷(Sea cucumber saponins,SCS) 0.04 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 萜类 11 6 海绵 Penares sp. 硫酸戊内酯A1(Penarolide sulfates A1) 0.001 2 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 大环内酯类 12 7 硫酸戊内酯A2(Penarolide sulfates A2) 0.001 5 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 8 硫代戊二酸甲酯A(Penasulfate A) 0.000 14 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 9~11 Penares schulzei Schulzeines A~C 0.048~0.17 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 生物碱 13 12 Ianthella sp. Iantheran A 0.37 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 苯并呋喃类 14 13 Lendenfeldia chondrodes 1-脱氧野尻霉素6-磷酸(1-Deoxynojirimycin-6-phosphate) Ki 0.83 μmol·L-1(未知) 脱氧野尻霉素衍生物 15 14 N-甲基-1-脱氧野尻霉素6-磷酸(N-Methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin-6-phosphate) Ki 6 600 μmol·L-1(未知) 15 Haliclona sp. 93-111 1,4-二脱氧-1,4-亚氨基-D-阿拉伯糖醇(1, 4-Dideoxy-1, 4-imino-D-arabinitol) 0.000 16 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多羟基吡咯烷衍生物 16 16 Callyspongia truncata Callyspongynic acid 0.000 25 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多炔类 17 17 Corticatic acid A 0.000 16 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 18 Petrosynol 0.004 08 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 19 海鞘 Synoicum macroglossum Tiruchanduramine 0.078 2 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 生物碱 18 表 2 海洋藻类来源的AGIs
化合物 海洋藻类 化合物来源 AGIs IC50 化合物种类 参考文献 20 褐藻 Ecklonia stolonifera 褐藻E. stolonifera甲醇提取物(Methanolic extract of E. stolonifera,MEE) 0.022 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多酚 19 21 Ishige okamurae 二邻羟基香豆酚(Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol,DPHC) 160 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多酚 20 22 Ecklonia cava 二鹅掌菜酚(Dieckol) 240 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多酚 21 23 Sargassum patens 2-(4-(3,5-二羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二羟基苯氧基)苯-1,3,5-三醇[2-(4-(3, 5-Dihydroxyphenoxy)-3, 5- dihydroxyphenoxy) benzene-1, 3, 5-triol,DDBT] 0.114 g·L-1(鼠胰腺,麦芽糖底物) 0.025 4 g·L-1(鼠胰腺,蔗糖底物) 多酚 22 24 Padinaboergesenii Padinolic acid - 脂肪酸 22 25 Ascophyllum nodosum 褐藻糖胶(Fucoidan) 0.013~0.047 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多糖 24 26 Macrocystis angustifolia 4-羟基苯乙醇[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)phenol] 0.278 23 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多酚 28 27 4-二羟基苯乙醇[4-(1, 2-Dihydroxyethyl)phenol] 0.335 76 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 28 Ecklonia stolonifera、Eisenia bicyclis 间苯三酚(Phloroglucinol) 0.141 2 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多酚 29 29 二氧萘甲醚(Dioxinodehydroeckol) 0.034 6 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 30 鹅掌菜酚(Eckol) 0.022 8 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 31 红藻 Grateloupiaelliptica 2,4,6-三溴苯酚(2, 4, 6-Tribromophenol) 60.3 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 110.4 μmol·L-1(嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌) 多酚 30 32 2,4-二溴苯酚(2, 4-Dibromophenol) 130.3 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 230.3 μmol·L-1(嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌) 33 Symphyocladia latiuscula 双(2,3,6-三溴-4,5-二羟基苄基)醚(Bis(2, 3, 6-tribromo-4, 5-dihydroxybenzyl) ether) 0.03 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多酚 31 34 Odonthalia corymbifera 4-溴-2,3-二羟基-6-羟甲基苯基2,5- 二溴-6-羟基-3-羟甲基苯基醚(4-Bromo-2, 3-dihydroxy-6-hydroxy methylphenyl-2, 5-dibromo-6-hydroxy- 25 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 醚类 32 35 双(2,3-二溴-4,5-二羟基苄基)醚[Bis(2, 3-dibromo-4, 5-dihydroxybenzyl) ether] 0.098 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 醚类 36 2,3-二溴-4,5-二羟基苄醇(2, 3-Dibromo-4, 5-dihydroxybenzyl alcohol) 89 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 37 绿藻 Chlorella ellipsoidea all-E-Lutein 70 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 类胡萝卜素 33 38 9Z-玉米黄质(9Z-Zeaxanthin) 53.5 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 40 ELP-3 0.36 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 多糖 34 40 ELP-4 0.58 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 41 Codium dwarkense Dwarkenoic acid 0.003 47 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 甾醇 34 42 Androst-5-en-3β-ol 0.005 32 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 43 Ergosta-5, 25-dien-3β-ol 0.003 9 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 44 7-Hydroxystigmasta-4, 25-dien-3- 0.009 09 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 45 one-7-O-β-D-fucopyranoside 0.016 89 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 46 8-7-Hydroxystigmasta-4, 25-dien-3-one 0.020 12 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 47 Stigmasta-5, 25-dien-3β-ol 0.003 31 g·L-1(酿酒酵母) 表 3 海洋微生物来源的AGIs
化合物 海洋微生物 化合物来源 AGIs IC50 化合物种类 参考文献 48 真菌 Aspergillus aculeatus CRI32304 (海绵Xestospongia testudinaria) Aspergillusol A 465 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 1 060 μmol·L-1(嗜热脂肪芽孢杆菌) 酪氨酸代谢物 37 49 Penicillium chermesinum (ZH4-E2) Chermesinones A 24.5 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) -联苯类 38 50 (秋茄Kandeliacandel) 6'-O-去甲基三联苯林(6'-O-Desmethylterphenyllin) 0.9 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 51 3-羟基-6'-O-去甲基三联苯林(3-Hydroxy-6'-O-desmethylterphenyllin) 4.9 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 52 3, 3''-二羟基-6'-O-去甲基三联苯林(3, 3''-Dihydroxy-6'-O-desmethylterphenyllin) 2.5 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 54 Eurotium rubrum SH-823 Eurothiocin A 17.1 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 苯并 39 54 (珊瑚Sarcophyton sp.) Eurothiocin B 42.6 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 呋喃类 55 红树林真菌B60 (老鼠簕Acanthus ilicifolius) 硝基苯基葡萄糖苷(Nitrophenyl glucoside) 160.3 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 硝基苯糖苷 40 56 红树林真菌Xylaria sp. BL321 (老鼠簕Acanthus ilicifolius) 07H239-A 6.54 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) 萜类 41-42 57 单胞菌 Streptomyces sp. OUCMDZ-3434 Wailupemycins H 19.7 μmol·L-1(鼠胰腺) - 43 58 (浒苔Enteromorphaprolifera) Wailupemycins I 8.3 μmol·L-1(鼠胰腺) 59 真菌 Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 (浒苔Enteromorphaprolifera) Diorcinol J 117.3 μmol·L-1(酿酒酵母) - 44 -
[1] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会, 国家基层糖尿病防治管理办公室. 国家基层糖尿病防治管理手册(2019)[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2019, 58(10): 713. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2019.10.003 [2] HEDRINGTON MS, DAVIS SN. Considerations when using alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J]. Exp Opin Pharmacother, 2019, 20(18): 2229-2235. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1672660 [3] LIU ZY, MA ST. Recent advances in synthetic α-glucosidase inhibitors[J]. Chem Med Chem, 2017, 12(11): 819-829. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201700216 [4] 裴丽, 罗艳, 黄显金, 等. 米格列醇的临床不良反应及合理用药[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2014, 17(7): 901-903. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYLC201407026.htm [5] SCOTT LJ, SPENCER CM. Miglitol: A review of its therapeutic potential in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Drugs, 2000, 59(3): 521-549. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059030-00012 [6] 黄欣欣, 罗艳, 裴丽, 等. 阿卡波糖不良反应及处置措施研究进展[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2015, 18(3): 338-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYLC201503026.htm [7] 庞力超, 吴桂林, 林红坤, 等. 阿卡波糖片与伏格列波糖片的不良反应分析及对患者生活质量的影响[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2018, 31(7): 1023-1026. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4337.2018.07.034 [8] 王成, 张国建, 刘文典, 等. 海洋药物研究开发进展[J]. 中国海洋药物, 2019, 38(6): 35-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYYW201906007.htm [9] NGUYEN TH, UM BH, KIM SM. Two unsaturated fatty acids with potent α-glucosidase inhibitory activity purified from the body wall of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus)[J]. J Food Sci, 2011, 76(9): H208-H214. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02391.x [10] NGUYEN TH, KIM SM. α-Glucosidase inhibitory activities of fatty acids purified from the internal organ of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicas[J]. J Food Sci, 2015, 80(4): H841-H847. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12810 [11] FU X, WEN M, HAN X, et al. Effect and potential mechanism of action of sea cucumber saponins on postprandial blood glucose in mice[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2016, 80(6): 1081-1087. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2016.1153950 [12] NAKAO Y, MAKI T, MATSUNAGA S, et al. Penasulfate A, a new alpha-glucosidase inhibitor from a marine sponge Penares sp[J]. J Nat Prod, 2004, 67(8): 1346-1350. doi: 10.1021/np049939e [13] TAKADA K, UEHARA T, NAKAO Y, et al. Schulzeines A-C, new alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from the marine sponge Penares schulzei[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126(1): 187-193. doi: 10.1021/ja037368r [14] OKAMOTO Y, OJIKA M, SUZUKI S, et al. Iantherans A and B, unique dimeric polybrominated benzofurans as Na, K-ATPase inhibitors from a marine sponge, Ianthella sp[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2001, 9(1): 179-183. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0896(00)00234-0 [15] SAKAI R, KAMIYA H. 1-Deoxynojirimycin derivatives from the marine sponge Lendenfeldia chondrodes[J]. J Antibiot (Tokyo), 2006, 59(8): 507-511. doi: 10.1038/ja.2006.71 [16] SALUDES JP, LIEVENS SC, MOLINSKI TF. Occurrence of the α-glucosidase inhibitor 1, 4-dideoxy-1, 4-imino-D-arabinitol and related iminopentitols in marine sponges[J]. J Nat Prod, 2007, 70(3): 436-438. doi: 10.1021/np060551o [17] NAKAO Y, UEHARA T, MATSUNAGA S, et al. Callyspongynic acid, a polyacetylenic acid which inhibits alpha-glucosidase, from the marine sponge Callyspongia truncata[J]. J Nat Prod, 2002, 65(6): 922-924. doi: 10.1021/np0106642 [18] RAVINDER K, VIJENDER REDDY A, KRISHNAIAH P, et al. Isolation and synthesis of a novel β-carboline guanidine derivative tiruchanduramine from the Indian ascidian Synoicum macroglossum[J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 2005, 46(33): 5475-5478. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.06.060 [19] IWAI K. Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of polyphenols in brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera in genetically diabetic KK-Ay mice[J]. Plant Foods Hum Nutr, 2008, 63(4): 163-169. doi: 10.1007/s11130-008-0098-4 [20] HEO SJ, HWANG JY, CHOI JI, et al. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol isolated from Ishige okamurae, a brown algae, a potent α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitor, alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic mice[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2009, 615(1/2/3): 252-256. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20093198906.html [21] LEE SH, PARK MH, HEO SJ, et al. Dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava inhibits α-glucosidase and α-amylase in vitro and alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2010, 48(10): 2633-2637. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.06.032 [22] KAWAMURA-KONISHI Y, WATANABE N, SAITO M, et al. Isolation of a new phlorotannin, a potent inhibitor of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes, from the brown alga Sargassum patens[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2012, 60(22): 5565-5570. doi: 10.1021/jf300165j [23] LO PIPARO E, SCHEIB H, FREI N, et al. Flavonoids for controlling starch digestion: structural requirements for inhibiting human α-amylase[J]. J Med Chem, 2008, 51(12): 3555-3561. doi: 10.1021/jm800115x [24] ALI L, KHAN AL, AL-BROUMI M, et al. New enzyme-inhibitory triterpenoid from marine macro brown alga Padina boergesenii allender & kraft[J]. Mar Drugs, 2017, 15(1): E19. doi: 10.3390/md15010019 [25] APOSTOLIDIS E, LEE CM. In vitro Potential of Ascophyllum nodosum Phenolic antioxidant-mediated α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition[J]. J Food Sci, 2010, 75(3): H97-H102. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01544.x [26] GABBIA D, DALL'ACQUA S, DI GANGI I, et al. The phytocomplex from Fucus vesiculosus and Ascophyllum nodosum controls postprandial plasma glucose levels: An in vitro and in vivo study in a mouse model of NASH[J]. Mar Drugs, 2017, 15(2): 41. doi: 10.3390/md15020041 [27] KIM KT, RIOUX LE, TURGEON SL. Alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibition is differentially modulated by fucoidan obtained from Fucus vesiculosus and Ascophyllum nodosum[J]. Phytochemistry, 2014, 98: 27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.12.003 [28] RENGASAMY KRR, ADEROGBA MA, AMOO SO, et al. Macrocystis angustifolia is a potential source of enzyme inhibitors linked to type 2 diabetes and dementia[J]. J Appl Phycol, 2014, 26(3): 1557-1563. doi: 10.1007/s10811-013-0171-8 [29] MOON HE, ISLAM N, AHN BR, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and α-glucosidase inhibitory Phlorotannins from edible brown algae, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2011, 75(8): 1472-1480. doi: 10.1271/bbb.110137 [30] KIM KY, NAM KA, KURIHARA H, et al. Potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitors purified from the red alga Grateloupia elliptica[J]. Phytochemistry, 2008, 69(16): 2820-2825. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.09.007 [31] KURIHARA H, MITANI T, KAWABATA J, et al. Inhibitory Potencies of Bromophenols from Rhodomelaceae Algae against alpha-glucosidase activity[J]. Fisheries Sci, 1999, 65(2): 300-303. doi: 10.2331/fishsci.65.300 [32] KURIHARA H, MITANI T, KAWABATA J, et al. Two new bromophenols from the red alga Odonthalia corymbifera[J]. J Nat Prod, 1999, 62(6): 882-884. doi: 10.1021/np980324p [33] QI J, KIM SM. Α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of lutein and Zeaxanthin purified from green alga Chlorella ellipsoidea[J]. J Ocean Univ China, 2018, 17(4): 983-989. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3465-2 [34] ZHANG LX, ZHANG N, LI JH, et al. New α-glucosidase inhibitory polysaccharides isolated from marine green algae enteromorpha linza[J]. Adv Mater Res, 2013, 634: 1010-1015. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036897224910_9997.html [35] ALI L, KHAN AL, AL-KHARUSI L, et al. New α-glucosidase inhibitory triterpenic acid from marine macro green alga Codium dwarkense boergs[J]. Mar Drugs, 2015, 13(7): 4344-4356. doi: 10.3390/md13074344 [36] 张哲, 王旻, 尹鸿萍, 等. 螺旋藻中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的提取及动力学[J]. 生物加工过程, 2008, 6(3): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2008.03.007 [37] INGAVAT N, DOBEREINER J, WIYAKRUTTA S, et al. Aspergillusol A, an α-glucosidase inhibitor from the marine-derived Fungus Aspergillus aculeatus[J]. J Nat Prod, 2009, 72(11): 2049-2052. doi: 10.1021/np9003883 [38] HUANG HB, FENG XJ, XIAO ZE, et al. Azaphilones and p-terphenyls from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium chermesinum (ZH4-E2) isolated from the South China Sea[J]. J Nat Prod, 2011, 74(5): 997-1002. doi: 10.1021/np100889v [39] LIU ZM, XIA GP, CHEN SH, et al. Eurothiocin A and B, sulfur-containing benzofurans from a soft coral-derived fungus Eurotium rubrum SH-823[J]. Mar Drugs, 2014, 12(6): 3669-3680. doi: 10.3390/md12063669 [40] SHAO CL, GUO ZY, XIA XK, et al. Five nitro-phenyl compounds from the South China Sea mangrove fungus[J]. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2007, 9(7): 643-648. doi: 10.1080/10286020600979753 [41] SONG Y, WANG J, HUANG H, et al. Four eremophilane sesquiterpenes from the mangrove endophytic fungus Xylaria sp. BL321[J]. Mar Drugs, 2012, 10(2): 340-348. http://www.biomedsearch.com/attachments/00/22/41/28/22412805/marinedrugs-10-00340.pdf [42] SONG YX, WANG J, LI SW, et al. Metabolites of the mangrove fungus Xylaria sp. BL321 from the South China Sea[J]. Planta Med, 2012, 78(2): 172-176. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1280347 [43] LIU W, WANG LP, WANG B, et al. Diketopiperazine and diphenylether derivatives from marine algae-derived Aspergillus versicolor OUCMDZ-2738 by epigenetic activation[J]. Mar Drugs, 2018, 17(1): E6. doi: 10.3390/md17010006 [44] CHEN ZB, HAO JJ, WANG LP, et al. New α-glucosidase inhibitors from marine algae-derived Streptomyces sp. OUCMDZ-3434[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 20004. doi: 10.1038/srep20004 [45] 黄帝内经素问[M]. 田代华, 整理. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2005. [46] 付先军, 王振国, 王长云, 等. 海洋中药的内涵与外延探讨[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2016, 18(12): 2034-2042. doi: 10.11842/wst.2016.12.002 [47] 冯学珍, 覃慧逢, 赵丽婷, 等. 食用海藻中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的筛选及抑制动力学[J]. 食品工业, 2019, 40(6): 195-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPGY201906050.htm [48] 延海莹, 刘盟梦, 左思琦, 等. 基于BP神经网络的牡蛎α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂活性肽制备工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技, 2017, 38(9): 206-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPKJ201709031.htm [49] 景永帅, 张丹参, 张瑞娟, 等. 提取方法对北沙参多糖性质及生物活性的影响[J]. 食品与机械, 2017, 33(10): 149-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPJX201710034.htm [50] 龙康候, 巫忠德. 海洋天然产物化学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984. [51] 张姣姣. 天然产物中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的研究进展[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2019, 49(3): 62-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QXSZ201903015.htm -





 下载:
下载: