Study on the Mechanism of Jiangzhi Mai'an Granule in Treating Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Network Pharmacology
doi: 10.14148/j.issn.1672-0482.2021.0096
-
摘要:
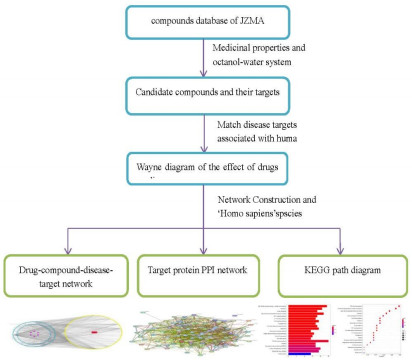
目的 采用网络药理学方法筛选降脂脉安颗粒(JZMA)的主要活性成分和作用靶点, 探讨其治疗非酒精性脂肪肝(NAFLD)的潜在作用机制。 方法 借助中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)中的脂水分配系数(ALogP)和药物相似性(DL)参数设置, 收集降脂脉安颗粒中各个药物的化学成分, 通过靶点预测网站服务器(UniProt)与人类基因数据库(Genecard)、人类孟德尔遗传数据库(OMIM)的整合来获取降脂脉安颗粒治疗非酒精性脂肪肝的作用靶点和疾病基因, 运用STRING在线工具构建蛋白互相作用(PPI)网络, 并借助Cytoscape 3.6.0构建"中药-成分-疾病-靶点"网络。利用Cytoscape3.7.2软件进行网络拓扑分析, 运用MCODE插件筛选出关键基因, 并采用STRING数据库与R 3.6.3软件进行基因本体(GO)分类富集和基于京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)通路富集分析。 结果 共得到283个潜在活性成分, 包括槲皮素(quercetin)、芹菜素(apigenin)、山柰酚等关键化合物; 经拓扑分析, 获得13个核心靶点、6个基因簇和4个核心基因CASP9、PTGS2、SLC2A4、OPRD1, 它们主要参与PI3K/Akt、AGE-RAGE、FOXO、IL-17、HIF-1信号通路等。 结论 网络药理学分析有助于揭示JZMA治疗NAFLD的主要物质基础, 预测了其多层次、多靶点和多途径的潜在作用机制, 为拓展临床应用提供了科学依据。 Abstract:OBJECTIVE To screen the main active components and action targets of Jiangzhi Mai'an granule by network pharmacology, and to explore its potential mechanism in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD). METHODS With the help of the parameter setting of lipid-water partition coefficient(ALogP) and drug similarity(DL) in traditional Chinese medicine system pharmacology database and analysis platform(TCMSP), the chemical components of each drug in Jiangzhi Mai'an granule were collected. The target and disease genes of Jiangzhi Mai'an granule in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver were obtained by integrating the target prediction website server(uniprot) with human gene database(Genecard) and human Mendelian genetic database(OMIM). The protein interaction(PPI) network was constructed by using STRING online tool, and the "traditional Chinese medicine-component-disease-target" network was constructed with the help of Cystoscap 3.6.0. In addition, Cytoscape 3.7.2 software was used for network topology analysis, MCODE plug-in was used to screen key genes, and STRING database and R3.6.3 software were used for gene ontology(GO) classification and enrichment analysis based on Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes(KEGG) pathway. RESULTS A total of 283 potentially active components were obtained, including quercetin, apigenin, kaempferol and other key compounds. Through topological analysis, 13 core targets, 6 gene clusters and 4 core gene CASP9, PTGS2, SLC2 A4, OPRD1 were obtained, which are mainly involved in PI3 K/Akt, AGE-RAGE, FOXO, IL-17, HIF-1 signal pathway and so on. CONCLUSION The analysis of network pharmacology is helpful to reveal the main material basis of Jiangzhi Mai'an granule in the treatment of NAFLD, predict its potential mechanism of multi-level, multi-target and multi-pathway, and provide a scientific basis for expanding clinical application. -
Table 1. Basic information of key compounds of JZMA (target number≥ 30)
No. ID Chemical compound Target number Main target Source of TCM 1 MOL000098 Quercetin 143 PTGS1、AR、PPAR、PRSS1、AKT1、RXRA Astragali Radix、Crataegi Fructus、Nelumbinis Folium 2 MOL000008 Apigenin 72 PTGS2、AR、PRSS1、FOS、AKT1、IL2 Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix 3 MOL000390 Daidzein 65 PTGS1、ESR1、FOS、MTTP、IL4、AHR Astragali Radix 4 MOL000422 Kaempferol 55 AHR、JUN、STAT1、PPARG、SELE、AKT1 Astragali Radix、Crataegi Fructus、Nelumbinis Folium 5 MOL000006 Luteolin 54 IL2、JUN、PTGS1、PTGS2、AKT1、IL4 Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix、Hordei fructus Germinatus 6 MOL007154 Tanshinone ⅡA 39 ESR1、PPARG、AR、ESR1、ADRB2、PTGS2 Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix 7 MOL000378 7-O-methylisom ucronulatol 36 NOS2、KCNH2、PTGS2、CHRM3、KCNH2、ADRB1 Astragali Radix 8 MOL002008 Myricetin 33 PTGS2、FYN、BAX、STAT3、IL6、PPARG Nelumbinis Folium 9 MOL007091 Dan-shexinkum B 32 NOS2、PTGS2、PPARG、CHRM3、HTR3A、ESR2 Astragali Radix 10 MOL007099 Dihydroisotan shinonⅠ 32 NOS2、KCNH2、PTGS2、CHRM3、HTR3A、PPARG Astragali Radix 11 MOL000392 Form ononetin 31 NOS2、PTGS2、IL4、PPARG、ESR2、PKIA Astragali Radix 12 MOL000472 Emodin 30 PTGS2、PPARG、FLT1、MMP9、CASP3、CSF2 Cassiae Semen -
[1] MOORE JB. From sugar to liver fat and public health: Systems biology driven studies in understanding non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis[J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2019, 78(3): 290-304. doi: 10.1017/S0029665119000570 [2] ZHOU JH, CAI JJ, SHE ZG, et al. Noninvasive evaluation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Current evidence and practice[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(11): 1307-1326. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i11.1307 [3] INOUE M, HAYASHI A, TAGUCHI T, et al. Effects of canagliflozin on body composition and hepatic fat content in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2019, 10(4): 1004-1011. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12980 [4] PERUMPAIL BJ, KHAN MA, YOO ER, et al. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(47): 8263-8276. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8263 [5] DIEHL AM, DAY C. Cause, pathogenesis, and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(21): 2063-2072. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1503519 [6] NASR P, IGNATOVA S, KECHAGIAS S, et al. Natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective follow-up study with serial biopsies[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2018, 2(2): 199-210. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1134 [7] SUN JG, WU JF, YANG J, et al. Clinical observation on 100 cases of fatty liver treated with Jiangzhi Mai'an granule and rhubarb umbilical application[J]. Hebei Tradit Chin Med, 2003, 25 (7): 494-496. [8] PENG HP, YANG J, WU JF, et al. Clinical study on the treatment of 40 cases of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with Jiangzhimai'an granule[J]. Jiangsu Tradit Chin Med, 2014, 46 (5): 32-33. [9] JIN TQ, ZHU HR. Study on the quality standard of Jiangzhimai'an granules[J]. Asia Pacif Tradit Med, 2015, 11 (15): 42-46. [10] YANG M, CHEN JL, XU LW, et al. Navigating traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology and computational tools[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2013, 2013: 731969. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.781.4657&rep=rep1&type=pdf [11] YANG Y, LI Y, WANG J, et al. Systematic investigation of Ginkgo biloba leaves for treating cardio-cerebrovascular diseases in an animal model[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2017, 12(5): 1363-1372. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00762 [12] ZENG L, YANG K, GE J. Uncovering the pharmacological mechanism of Astragalus Salvia compound on pregnancy-induced hypertension syndrome by a network pharmacology approach[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 16849. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17139-x [13] ZHANG RZ, ZHU X, BAI H, et al. Network pharmacology databases for traditional Chinese medicine: Review and assessment[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 123. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00123 [14] XU WQ, QIN XM, LIU YT. Mechanism of Huangqi Jianzhong Decoction in treating chronic atrophic gastritis based on network pharmacology[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drug, 2018, 49(15): 3550-3561. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZCYO201815012.htm [15] SHAWKY E. Prediction of potential cancer-related molecular targets of North African plants constituents using network pharmacology-based analysis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2019, 238: 111826. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111826 [16] LEE AY, PARK W, KANG TW, et al. Network pharmacology-based prediction of active compounds and molecular targets in Yijin-Tang acting on hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 221: 151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.027 [17] FAN RR, LUO ZQ, TANG LJ, et al. Analysis of Xiaoqinglong decoction for treatment of bronchial asthma based on network pharmacology[J]. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharm, 2019, 30(1): 52-59. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZYXY201901009.htm [18] YUAN N, GONG L, TANG K, et al. An integrated pharmacology-based analysis for antidepressant mechanism of Chinese herbal formula Xiao-Yao-San[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 284. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00284 [19] LI L, QIU H, LIU M, et al. A network pharmacology-based study of the molecular mechanisms of Shaoyao-Gancao decoction in treating Parkinson's disease[J]. Interdiscip Sci, 2020, 12(2): 131-144. doi: 10.1007/s12539-020-00359-7 [20] GUAN QY, WANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Network pharmacology-based mechanism of Xiao Xianxiongtang in treatment of coronary heart disease[J]. Chin J Exper Tradit Med Formul, 2020, 26(5): 152-161. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010482520301906 [21] ZHANG M, YUAN Y, ZHOU W, et al. Network pharmacology analysis of Chaihu Lizhong Tang treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Comput Biol Chem, 2020, 86: 107248. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107248 [22] GAO Y, WU D, TIAN JS, et al. Mechanism of network pharmacology of Xiaoyao powder and Kaixin powder in treating depression with "Same disease with different treatments"[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drug, 2018, 49(15): 3483-3492. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZCYO201815004.htm [23] WU R, LI XY, CAI FF, et al. Effective mechanism of Bushen Jianpi Decoction in the treatment of liver cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2018, 33(9): 4134-4139. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY201809109.htm [24] WU JY, ZHANG L, XIE YZ, et al. Study on the mechanism of Wendan decoction in the treatment of coronary heart disease based on network pharmacology[J]. China Pharm, 2018, 29(23): 3227-3232. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGYA201823013.htm [25] WANG BL, LI YW. Research on network pharmaconlogy of action mechanism of Xianglian pills[J]. Chin Pharm J, 2018, 53(24): 2079-2089. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGYX201824003.htm [26] GE Q, CHEN L, YUAN Y, et al. Network pharmacology-based dissection of the anti-diabetic mechanism of Lobelia chinensis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 347. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00347 [27] WANG N, ZHU F, SHEN M, et al. Network pharmacology-based analysis on bioactive anti-diabetic compounds in Potentilla discolor bunge[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2019, 241: 111905. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111905 [28] WANG W, LIU T, YANG L, et al. Study on the multi-targets mechanism of triphala on cardio-cerebral vascular diseases based on network pharmacology[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 116: 108994. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108994 [29] CUI Q, ZHANG YL, MA YH, et al. A network pharmacology approach to investigate the mechanism of Shuxuening injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 257: 112891. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112891 [30] CAI MC, YU CQ. Mechanism of Jinzhen oral liquid in treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 based on network pharmacology[J]. J Pharm Pract, 2020, 38(3): 193-201. [31] KONG Y, WU HW, CHEN Y, et al. Mechanism of Tanreqing Injection on treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drug, 2020, 51(7): 1785-1794. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/343559748_A_Network_Pharmacology-based_Analysis_of_the_Molecular_Mechanism_of_Tanreqing_in_the_Treatment_of_the_Coronavirus_Disease_2019_COVID-19 [32] SONG YJ, BAO JM, ZHOU LY, et al. An analysis of the anti-neuropathic effects of qi she pill based on network pharmacology[J]. Evid Based Complement Altern Med, 2020, 2020: 7193832. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/341168996_An_Analysis_of_the_Anti-Neuropathic_Effects_of_Qi_She_Pill_Based_on_Network_Pharmacology [33] ZHANG T, JIANG WJ, WU JF, et al. Molecular mechanism of Jinqi Shenqi pills in treatment of myopia based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics[J]. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med, 2019, 46(5): 916-919, 1118. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-LNZY201905006.htm [34] ZHANG L, SHI X, HUANG Z, et al. Network pharmacology approach to uncover the mechanism governing the effect of Radix achyranthis bidentatae on osteoarthritis[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2020, 20(1): 121. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02909-4 [35] GUO S, WU WX, XIE H, et al. Molecular mechanism of Bufei Huoxue Capsule on COVID-2019 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drug, 2020, 51(9): 2307-2316. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/342297957_Exploring_the_Mechanisms_of_Lian_Hua_Qing_Wen_Capsule_against_COVID-19_by_Network_Pharmacology_and_Molecular_Docking_Approach [36] FAN YH, OU HY, WANG HY, et al. Analysis on mechanism of Yinchen Wulingsan based on network pharmacology[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formul, 2018, 24(11): 193-200. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZSFX201811032.htm [37] ZHENG Q, HOU W. Molecular mechanism of coptidis rhizoma-euodiae fructus for gastric cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formul, 2020, 26(7): 204-210. [38] CHAI LL, SUN MY, YAO HZ, et al. Mechanism of Guanxinning tablet in the treatment of coronary heart disease with stable angina pectoris based on network pharmacology[J]. Chin Tradit Pat Med, 2019, 41(4): 933-936. [39] ZHONG ZS, ZHANG W, YE ZH, et al. Effect of YiqiHuayuJiedu decoction on chronic atrophic gastritis and its mechanism based on network pharmacology[J]. Pharm Clin Chin Mater Med, 2019, 35(3): 141-144. [40] STEENSELS S, QIAO J, ZHANG Y, et al. Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 9 traffics mitochondrial short-chain fatty acids toward de novo lipogenesis and glucose production in the liver[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72(3): 857-872. doi: 10.1002/hep.31409 [41] ZHANG C, LI CP, NIE J. Influence of quercetin on expressions of stearyl coenzyme A saturated enzyme 1 and liver X receptor α in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease model rats[J]. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol, 2017, 31(8): 807-814. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YLBS201708006.htm [42] HE HX, KONG LX, LI XY, et al. Kaempferol vs lindley euqatorium herb total flavonoid for lyperlipemia and hemorheological parameters in rats[J]. J Third Mil Med Univ, 2014, 36(11): 1187-1189. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSDX201411023.htm [43] XI JJ, ZHUANG RX, WANG FG, et al. Therapeutic effect and mechanisms of apigenin on non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats[J]. Chin Archi Tradit Chin Med, 2014, 32(7): 1636-1638. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZYHS201407035.htm [44] LI XX, LU XY, ZHANG SJ, et al. Sodium tanshinone ⅡA sulfonate ameliorates hepatic steatosis by inhibiting lipogenesis and inflammation[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 111: 68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.019 [45] LIU T, XU QL, ZHAO Y. Inflammatory mechanism of emodin inhibiting lipid deposition in liver of NAFLD rats[C]. Nanning: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on liver Diseases of the WFCMS, 2015. [46] BESSONE F, RAZORI MV, ROMA MG. Molecular pathways of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development and progression[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(1): 99-128. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2947-0 [47] HELLMANN J, TANG Y, ZHANG MJ, et al. Atf3 negatively regulates Ptgs2/Cox2 expression during acute inflammation[J]. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 2015, 116/117: 49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2015.01.001 [48] LIU Q, GUO L, ZHANG S, et al. PRSS1 mutation: A possible pathomechanism of pancreatic carcinogenesis and pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Med, 2019, 25(1): 44. doi: 10.1186/s10020-019-0111-4 [49] JANCSO Z, ORACZ G, KUJKO AA, et al. Novel pathogenic PRSS1 variant p. Glu190Lys in a case of chronic pancreatitis[J]. Front Genet, 2019, 10: 46. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00046 [50] CAO Z, CEN HB, ZHENG CX, et al. Research progress on the regulation mechanism of fatty acid synthetase[J]. J Clin Exp Pathol, 2016, 322: 197-199. [51] LIU MX, GAO M, LI CZ, et al. Dicer1/miR-29/HMGCR axis contributes to hepatic free cholesterol accumulation in mouse non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2017, 38(5): 660-671. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.158 [52] ZHAO Z, XU D, WANG Z, et al. Hepatic PPARα function is controlled by polyubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation through the coordinated actions of PAQR3 and HUWE1[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(1): 289-303. doi: 10.1002/hep.29786 [53] YENIOVA AO, KUCUKAZMAN M, ATA N, et al. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is a strong predictor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2014, 61(130): 422-425. [54] KWILASZ AJ, GRACE PM, SERBEDZIJA P, et al. The therapeutic potential of interleukin-10 in neuroimmune diseases[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2015, 96: 55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.10.020 [55] PAREDES-TURRUBIARTE G, GONZALEZ-CHAVEZ A, PEREZ-TAMAYO R, et al. Severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with high systemic levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha and low serum interleukin 10 in morbidly obese patients[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2016, 16(2): 193-202. doi: 10.1007/s10238-015-0347-4 [56] ZHANG XN, ZHANG JP, XU SX, et al. Potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction for treatment of hypertension based on network pharmacology[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2018, 49(24): 5865-5875. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZCYO201824021.htm [57] ZHOU W, WU J, ZHU Y, et al. Study on the mechanisms of compound Kushen injection for the treatment of gastric cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2020, 20(1): 6. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2787-y [58] MENG Z, LIU X, WU J, et al. Mechanisms of compound Kushen injection for the treatment of lung cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2019, 2019: 4637839. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31275410 [59] BU DD, SU Z, ZHANG D, et al. Mechanism of Zuojin Pill in the treatment of gastric ulcer based on Network Pharmacology[J]. Chin Tradit Patent Med, 2019, 41(6): 1264-1271. [60] WU HY, ZHANG C, WANG ZH, et al. Network pharmacology-based analysis on the molecular biological mechanisms of Xin Hui Tong formula in coronary heart disease treatment[J]. Digit Chin Med, 2019, 2(2): 86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.dcmed.2019.09.003 [61] BORRELLI A, BONELLI P, TUCCILLO FM, et al. Role of gut microbiota and oxidative stress in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocarcinoma: Current and innovative therapeutic approaches[J]. Redox Biol, 2018, 15: 467-479. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.01.009 [62] CHEN Z, TIAN R, SHE Z, et al. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 152: 116-141. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.025 [63] AKTER MH, RAZZAQUE MA, YANG L, et al. Identification of a gene sharing a promoter and peroxisome proliferator-response elements with acyl-CoA oxidase gene[J]. PPAR Res, 2006, 2006: 71916. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Md_Abdur_Razzaque3/publication/6458480_Identification_of_a_Gene_Sharing_a_Promoter_and_Peroxisome_Proliferator-Response_Elements_With_Acyl-CoA_Oxidase_Gene/links/02e7e528a29c6bfd7f000000 [64] YANG M, HUANG Y, CHEN J, et al. Activation of AMPK participates hydrogen sulfide-induced cyto-protective effect against dexamethasone in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014, 454(1): 42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.033 [65] HUA YN, LU FA, WANG YF. HIF-1 related signaling pathway and its role in autoimmune diseases[J]. Chin J Imm, 2019, 35(8): 1013-1017. [66] CHEN J, BAI M, NING C, et al. Gankyrin facilitates follicle-stimulating hormone-driven ovarian cancer cell proliferation through the PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/cyclin D1 pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(19): 2506-2517. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.316 [67] ZENG L, ZHOU HY, TANG NN, et al. Wortmannin influences hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha expression and glycolysis in esophageal carcinoma cells[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(20): 4868-4880. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4868 [68] ZHOU XL, SHU L, LIAO Y, et al. Role of PI3K/AKT signal pathway in expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and glycolysis in colon cancer cells under hypoxia[J]. Acta Med Univ Sci Technol Huazhong, 2018, 47(2): 203-206. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-TJYX201802015.htm [69] WANG BF, TIAN PY, FENG K, et al. Role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2010, 18(30): 3175-3180. doi: 10.11569/wcjd.v18.i30.3175 [70] WANDRER F, LIEBIG S, MARHENKE S, et al. TNF-Receptor-1 inhibition reduces liver steatosis, hepatocellular injury and fibrosis in NAFLD mice[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(3): 212. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2411-6 [71] LEE AY, PARK W, KANG TW, et al. Network pharmacology-based prediction of active compounds and molecular targets in Yijin-Tang acting on hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 221: 151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.027 [72] CHEN WN, ZHU AS, CONG PW, et al. Molecular mechanism of Erchen Decoction in treatment of coronary heart disease based on network pharmacology[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drug, 2019, 50(2): 441-448. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZCYO201902025.htm -





 下载:
下载: